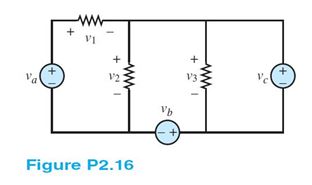
Use KVL to find the voltages v1,v2, and v3 in Figure P2.16. Assume that va = 2 V, vb = 4 V, and vc = 5 V.
What will be an ideal response?
Known quantities:
Va = 2 V, Vb = 4 V, Vc = 5 V
Find:
V1
V2
V3
Analysis:
Use KVL at the third loop.
V_3-V_c=0
V_3=V_c
V_3=5V
Use KVL at the second loop.
V_2 ?-V?_3-V_b=0
V_2=V_3+V_b
V_2=9V
Use KCL at the first loop.
V_a ?-V?_1-V_2=0
V_1=V_a-V_2
V_1=-7V
You might also like to view...
The central provisions of the Clayton Anti-Trust Act
A. included trade unions under the antimonopoly provisions of the Sherman Anti-Trust Act. B. declared that no single corporation could control more than 75 percent of a given industry. C. established minimum wage rates for goods produced in interstate commerce. D. outlawed corporate interlocking directorates and price discrimination against different purchasers. E. weakened regulations against interlocking directorates and private discrimination against different purchasers.
Mulching plants will insulate them from the cold and will protect them from drying out in the heat
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
For a more natural effect, the shape of the nail should conform to the:
What will be an ideal response?
During an AC performance test, an R-134a air conditioning system has a measured center duct outlet temperature of 59 degrees F. A manifold gage set shows low side pressure ranges between 35-45 psi and the high side pressure ranges from 250-400psi. Shop Temperature is 72 degrees F. What is most likely the cause?
a. The system has insufficient charge and may be leaking b. The system contains air with the refrigerant c. The TXV is restricted and not allowing enough refrigerant to flow d. The compressor is defective