In this graph for the marginal costs and benefits of pollution controls, at output level Q*, pollution control is ______.
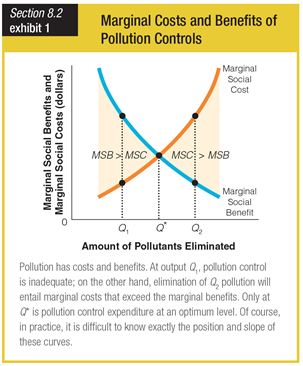
a. unnecessary
b. optimized
c. insufficient
d. excessive
b. optimized
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, an increase in government spending that increases aggregate demand from AD to AD1 will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ creating _____gap. 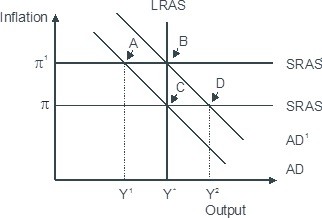
A. D; an expansionary B. B; no output C. B; expansionary D. A; a recessionary
The domestic demand curve, domestic supply curve, and world supply curves for a good are given in the above figure. All the curves are linear. Initially, the country allows imports. Then imports are banned
Calculate how consumer and producer surplus change because of the ban. Is the country better off with the ban on imports? Why?
The natural rate of unemployment is: a. equal to the seasonal unemployment
b. usually equal to 3 percent. c. the unemployment rate when none of the work force is unemployed for more than six weeks. d. the unemployment rate at which the economy is producing its potential GDP. e. defined by the government.
What gives the monopolistically competitive firm some degree of monopoly power?
a. differentiated products b. identical products c. high long-run economic profits d. zero long-run economic profits