Refer to the graph shown. Suppose an economy begins at point B but then adopts a contractionary monetary policy. In the short run, this policy would most likely: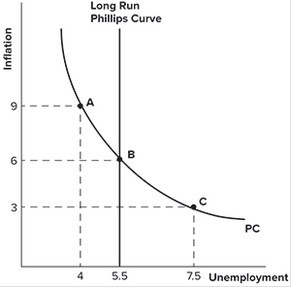
A. reduce inflation to 3 percent and reduce unemployment to 4 percent.
B. raise inflation to 9 percent and reduce unemployment to 4 percent.
C. reduce inflation to 3 percent and raise unemployment to 7.5 percent.
D. raise inflation to 9 percent and raise unemployment to 7.5 percent.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Billy is running a fast-food burger stand in his small community. If he is like other monopolistic competitors in short-run equilibrium which of the following would be true? a. His demand curve would be downward sloping
b. His marginal revenue curve would lie below his demand curve. c. He would be maximizing profits where his MC = MR. d. All of the above would be characteristics of Billy's burger stand.
Suppose the government's goal is to increase consumption in the year 2002 . Its two options are (1) an announced one-time $1 billion dollar tax cut for 2002 or (2) an announced permanent tax cut (2000 and thereafter) of $1 billion dollars starting in 2002. Which would more effectively achieve the government's goal?
a. the one-time tax rebate, if Friedman's permanent income hypothesis is correct b. the permanent tax cut, if Friedman's permanent income hypothesis is correct c. either option would do because each will increase consumption by the same amount d. the one-time tax rebate, if Duesenberry's relative income hypothesis is correct e. the permanent tax cut, if Duesenberry's relative income hypothesis is correct
According to the equation of exchange, if V = 10, P = 3, and Y = $100, then the money supply equals
A. $10. B. $15. C. $30. D. $150.
The recessionary expenditure gap associated with the recession of 2007-2009 resulted from:
A. the government's attempt to control hyperinflation. B. a major increase in personal and corporate taxes. C. a rapid decline in investment spending. D. a rapid increase in imports resulting from large tariff reductions.