If the economy in the graph shown is currently at point B, and the government enacts contractionary fiscal policy, in the short run the economy will most likely move to point:
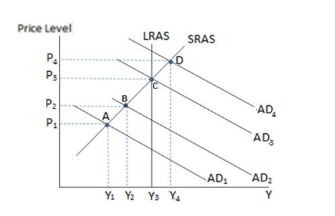
A. A
B. It is likely to be unaffected and stay at point B
C. C
D. D
A. A
You might also like to view...
Explain how a specific tax equal to the marginal harm of pollution can increase or decrease total welfare in a monopoly market
What will be an ideal response?
Which was NOT an argument of the protesters against the IMF, WTO, and the World Bank?
A. We are exploiting factory workers in poor countries. B. Our subsidized grain exports sold below cost in poor countries, driving local farmers out of business. C. Globalization is hurting the American standard of living. D. Globalization is lowering American wages and exporting high paying jobs.
During a study session for an economics exam with three other students, Peter Daltry commented on an example of a consumer who had to decide on number of slices of pizza and cups of Coca-Cola he would consume. Peter explained that "To maximize his
utility this consumer must equate the marginal utility per dollar for pizza and Coca-Cola." Was Peter's analysis correct? A) Peter described one of the conditions necessary for utility maximization. The consumer also must equate the marginal utility of pizza and the marginal utility of cups of Coca-Cola. B) Peter's statement is correct. C) Peter's statement is correct but we must also assume that the consumer is rational. D) Peter describes one of the conditions necessary for utility maximization. The second condition is that total spending on both goods must equal the amount available to be spent.
Adam Smith believed that the best way to promote the public interest was to
A. have the government produce most goods and services. B. let people pursue their own selfish interests. C. wait for individuals to set out to promote the public interest. D. get rid of the price mechanism.