Use Figure 9-7 to answer questions a-j
a. If there is no quota what is the domestic price of almonds and what is the quantity of almonds demanded by consumers?
b. If there is no quota how many kilos of almonds would domestic producers supply and what quantity would be imported?
c. If there is no quota what is the dollar value of consumer surplus?
d. If there is no quota what is the dollar value of producer surplus received by producers in Bragabong?
e. If there is no quota what is the revenue received by foreign producers who supply almonds to Bragabong?
f. With a quota in place what is the price that consumers of Bragabong must now pay and what is the quantity demanded?
g. With a quota in place what is the dollar value of consumer surplus? Are consumers better off?
h. With a quota in place what is the dollar value of producer surplus received by producers in Bragabong? Are domestic producers better off?
i. Calculate the revenue to foreign producers who are granted permission to sell in Bragabong after the imposition of the quota.
j. Calculate the deadweight loss as a result of the quota.
a. Price without a quota = $3 per kilo; quantity demanded = 36 million kilos
b. Quantity supplied by domestic producers when there is no quota = 14 million kilos; quantity imported = 22 million kilos
c. Consumer surplus without a quota = 1/2 × $6 × 36 million = $108 million
d. Domestic producer surplus without a quota = 1/2 × 14 million × $2.40 = $16.8 million
e. Revenue received by foreign producers when there is no quota =22 million × $3 = $66 million
f. Price with a quota = $4.00 per kilo; quantity demanded = 30 million kilos
g. Consumer surplus with a quota = 1/2 × $5 × 30 million = $75 million. No, consumers are worse off.
h. Domestic producer surplus with a quota = 1/2 × $3.40 × 20 million = $34 million. Yes, domestic producers are better off.
i. With a quota revenue to foreign producers = $4 × 10 million = $40 million
j. Deadweight loss = 1/2 × $1 × 6 million + 1/2 × $1 × 6 million = $6 million
You might also like to view...
Comparisons of economic activity over time should be made using:
A. nominal GDP per capita. B. current-dollar GDP. C. real GDP. D. nominal GDP adjusted for unemployment.
Controlling the quantity of money and interest rates to influence aggregate economic activity is called
A) foreign policy. B) monetary policy. C) fiscal policy. D) bank antitrust policy.
Suppose the United States initially has a trade deficit. Then U.S. firms increase their imports from Canada, financing that increase by borrowing from Canada
The current account deficit is now ________ and the capital and financial account surplus is now ________. A) larger; larger B) larger; smaller C) smaller; larger D) smaller; smaller
Refer to the figure below.________ inflation will eventually move the economy pictured in the diagram from short-run equilibrium at point ________ to long-run equilibrium at point ________, 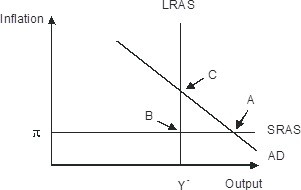
A. Rising; B; C B. Falling; A; C C. Falling; A; B D. Rising; A; C