Which of the following is NOT a reason for managers with quality?
a. Improvements in quality can lower costs.
b. Labor unions always support quality improvement efforts.
c. Improvements in quality can increase productivity.
d. All of these are correct.
e. None of these are correct.
B
You might also like to view...
Un sellado eficaz y permanente es uno de los métodos utilizado para evitar la entrada de polvo en los receptáculos mediante un sistema de conductos en una ubicación Clase II, División 2. Otra manera es:
a. un puente de conexión. b. un sistema de conductos horizontal no inferior a 10' (3,05 m) de longitud. c. un sistema de conductos vertical no inferior a 3' (0,60 m) de longitud. d. contratuercas doble.
Describe how we as consumers benefit from modern farming practices
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following statements is correct about sizing the bonding jumper on the load side of the service equipment?
A. It is sized from Table 250.66 in accordance with the rating of the overcurrent protective device in the service equipment. B. It is sized from Table 250.122 in accordance with the rating of the overcurrent protective device in the service equipment. C. It is sized from Table 250.102(C)(1) in accordance with the size of the service-entrance conductors on the supply side of the service. D. It is sized from Table 250.122 in accordance with the size of the service-entrance conductors on the supply side of the service.
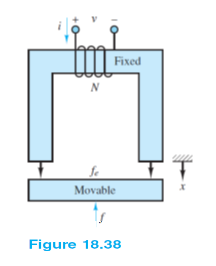
Calculate the current required to lift the load for the electromagnet of Example 18.9. Calculate the holding current required to keep the load in place once it has been lifted and is attached to the magnet.
Assume:
N = 700;
?0 = 4? × 10?7;
?r = 104 (equal for electromagnet and load);
initial distance (air gap) = 0.5 m;
magnetic path length of electromagnet = l1 = 0.80 m;
magnetic path length of movable load = l2 = 0.40 m;
gap cross-sectional area = 5 × 10?4 m2;
m = mass of load = 10 kg;
g = 9.8 m/s2.
Example 18.9
An electromagnet is used to collect and support a solid piece of steel, as shown in Figure 18.38. Calculate the starting current required to lift the load and the holding current required to keep the load in place once it has been lifted and is attached to the magnet. Assume that the cross-sectional areas of the electromagnet, load (bar), and air gap are equal.