As workforces become more educated in countries with comparative advantage in labor-intensive products, the comparative advantage for the production of those labor-intensive goods shifts:
A. away from countries with more cheap labor relative to other factors of production.
B. toward other countries with less cheap labor relative to the other factors of production.
C. toward countries with more capital for production.
D. toward other countries with more cheap labor relative to the other factors of production.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Refer to Figure 2-13. What is the opportunity cost of producing 1 ton of pineapples in Costa Rica?
A) 3/8 of a ton of coconuts B) 2/3 of a ton of coconuts C) 1 1/2 tons of coconuts D) 100 tons of coconuts
A person remodeling her house could obtain a loan from a
A) sales finance company. B) consumer finance company. C) business finance company. D) public finance company.
To test the theory that if the price of pens rises, then pen purchases fall, an economist would
A. collect data on the price of pens and the price of pencils because the two goods are substitutes. B. investigate whether people purchase more pens when their income rises. C. analyze data on pen purchases linked to the price of pens, holding other factors constant. D. ask his or her friends if they would buy fewer pens when the price rises.
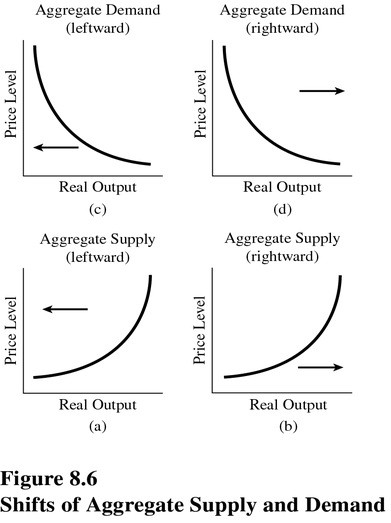 Choose the letter below that best represents the type of shift that would occur in the following situation in the United States: During the late 1990s, productivity in many U.S. industries increased because of technological advances. (See Figure 8.6.)
Choose the letter below that best represents the type of shift that would occur in the following situation in the United States: During the late 1990s, productivity in many U.S. industries increased because of technological advances. (See Figure 8.6.)
A. A. B. B. C. C. D. D.