Identify the anticodon sequences for an mRNA sequence that is 5?-AUG GGC ACU CAU-3?.
A. 3?AUG 5’ – 3’ GGC 5’ – 3’ ACU 5’ – 3’ CAU5?
B. 3?UAC 5’ – 3’ CCG 5’ – 3’ UGA 5’ – 3’ GUA5?
C. 5?AUG 3’ – 5’ GGC 3’ – 5’ ACU 3’ – 5’ CAU3?
D. 5?UAC 3’ – 5’ CCG 3’ – 5’ UGA 3’ – 5’ GUA3?
E. 3?TAC 5’ – 3’ CCG 5’ -5’ TGA 3’ – 5’ GTA 3?
B. 3?UAC 5’ – 3’ CCG 5’ – 3’ UGA 5’ – 3’ GUA5?
You might also like to view...
What kinds of general observations cause one to conclude that development is the result of variable gene activity?
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to the accompanying figure. Based on the phenotypes of the third generation, the genotype of the father in the second generation must be:
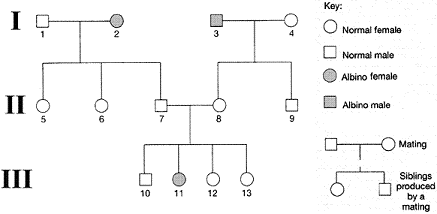
a. homozygous for albinism.
b. heterozygous for hair color.
c. heterozygous for albinism.
d. X-linked.
e. dominant
Which of the following statements about internal membranes in eukaryotic cells is false?
A) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes greatly increase a cell's total membrane area. B) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes provide an additional area for many metabolic processes to occur. C) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes form membranous compartments called organelles. D) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes standardize the internal environment of all cellular organelles.
The genes for zeste eyes and forked bristles are located on the X chromosome in Drosophila melanogaster. Both genes are recessive. A cross is made between a zeste-eyed female and a forked-bristled male. If 200 offspring from this cross were obtained,
what is the expected offspring's phenotype and sex? A) 100 forked female; 100 zeste male B) all wild type C) 50 wild female, 50 forked female; 50 zeste forked male, 50 zeste male D) 100 wild female; 100 zeste male E) 100 zeste female; 100 zeste forked male