Water at 180°C enters a bare, 15-m-long, 2.5-cm wrought iron pipe at 3 m/s. If air at 10°C flows perpendicular to the pipe at 12 m/s, determine the outlet temperature of the water. (Note that the temperature difference between the air and the water varies along the pipe.)
GIVEN
• Wrought-iron pipe with water flow inside and perpendicular air flow outside
• Water entrance temperature (TW,in) = 180°C
• Water velocity (VW) = 3 m/s
• Pipe length (L) = 15 m
• Pipe diameter (D) = 2.5 cm = 0.025 m
• Air temperature (Ta) = 10°C
• Air velocity (Va) = 12 m/s FIND
• Outlet temperature of the water (TW,out) ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state
• Air flow approaching pipe is negligible
• Thermal resistance of the pipe is negligible
• The pipe thickness can be neglected
SKETCH
Air Side:
The Reynolds number on the air side is

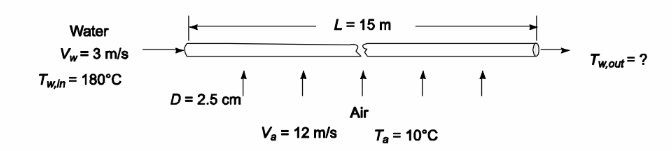
The Nusselt number is given by
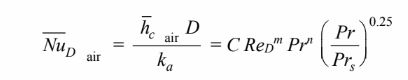
where C = 0.26, m = 0.6, and n = 0.37.
Note that the Prandtl number of air does not change appreciably between the air and water
temperatures. Therefore, Pr/Prs = 1.
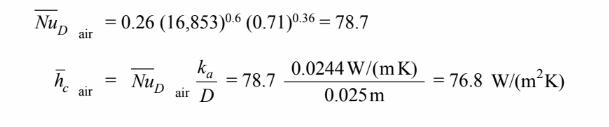
Water Side:
The Reynolds number based on the inlet properties is
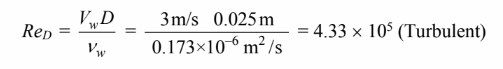
Applying
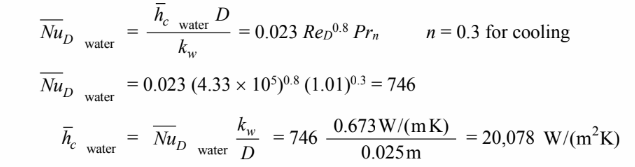
The overall heat transfer coefficient is
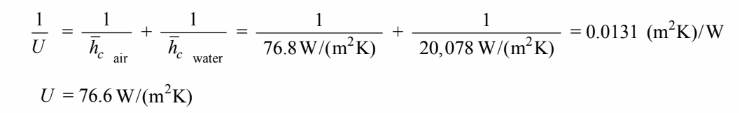
Let’s assume that the water temperature changes little from the pipe inlet to outlet. Since the air
temperature is constant and uniform, the heat transfer from the water is then analogous to the uniform
surface temperature analysis of may be applied
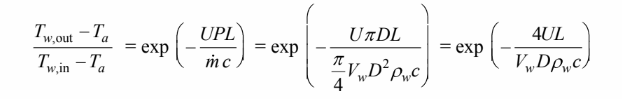
Solving for the water outlet temperature
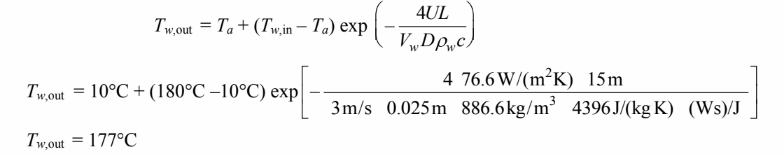
Therefore, the assumption that the water changes little from pipe inlet to outlet is valid.
COMMENTS
The average water temperature is 178.5°C. This is not different enough from the inlet temperature to
justify another iteration using the water properties at the average water temperature.
Note that the convective thermal resistance of the air is 99.6% of the total thermal resistance.
You might also like to view...
Very importantly, a hydraulic press can multiply
A) forces. B) pressures. C) energy. D) all of the above E) none of the above
For an ideal gas of a given mass, if the pressure remains the same and the volume increases,
a. the average kinetic energy of the molecules decreases. b. the average kinetic energy of the molecules stays the same. c. the average kinetic energy of the molecules increases. d. Nothing can be determined about the molecular kinetic energy.
A positron is the ______________of an electron
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Which of the beams is due to a high energy electron?
A) a B) b C) c D) all of the above E) none of the above