Use mathematical induction to prove the statement is true for all positive integers n.1 ? 2 + 2 ? 3 + 3 ? 4 + . . . + n(n + 1) = 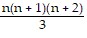
What will be an ideal response?
Answers may vary. Possible answer:
First, we show the statement is true when n = 1.
For n = 1, we get 1 ? 2 = 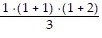
Since 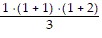 =
= 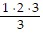 = 1 ? 2, P1 is true and the first condition for the principle of induction is satisfied.
= 1 ? 2, P1 is true and the first condition for the principle of induction is satisfied.
Next, we assume the statement holds for some unspecified natural number k. That is,
Pk: 1 ? 2 + 2 ? 3 + 3 ? 4 + . . . + k(k + 1) = 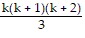 is assumed true.
is assumed true.
On the basis of the assumption that Pk is true, we need to show that Pk+1 is true.
Pk+1: 1 ? 2 + 2 ? 3 + 3 ? 4 + . . . + k(k + 1) + (k + 1)(k + 2) = 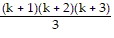
So we assume that 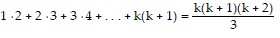 is true and add the next term,
is true and add the next term, 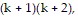 to both sides of the equation.
to both sides of the equation.
1 ? 2 + 2 ? 3 + 3 ? 4 + . . . + k(k + 1) + (k + 1)(k + 2) = 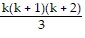 + (k + 1)(k + 2)
+ (k + 1)(k + 2)
1 ? 2 + 2 ? 3 + 3 ? 4 + . . . + k(k + 1) + (k + 1)(k + 2) = 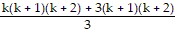
1 ? 2 + 2 ? 3 + 3 ? 4 + . . . + k(k + 1) + (k + 1)(k + 2) = 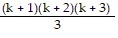
The last equation says that Pk+1 is true if Pk is assumed to be true. Therefore, by the principle of mathematical induction, the statement 1 ? 2 + 2 ? 3 + 3 ? 4 + . . . + n(n + 1) = 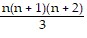 is true for all natural numbers n.
is true for all natural numbers n.
You might also like to view...
Solve for x.4-2x + 6 = 1
A. x = 0.25 B. x = -3 C. x = 3 D. x = 5
Write a formula for the nth term of the given geometric sequence. Do not use a recursion formula.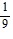 , -
, - 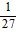 ,
, 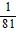 , -
, - 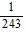 , ...
, ...
A. an = 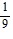 -
- 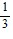 (n - 1)
(n - 1)
B. an = 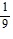
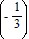 n - 1
n - 1
C. an = 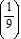 n - 1-
n - 1- 
D. an = 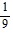 -
- 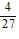 (n - 1)
(n - 1)
Find the indicated term of the sequence.an = 5n2(12n - 96); a6
A. -5400 B. -4320 C. 30,240 D. 31,320
Determine algebraically whether the function is even, odd, or neither.f(x) = 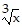
A. even B. odd C. neither