Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1.By widening the size of the domestic market, international trade permits companies to take advantage of longer production runs and increasing efficiencies such as mass production.
2.The theory of overlapping demands applies best to trade in manufactured goods.
3.Decreasing cost conditions lead to complete specialization in the production of the commodity of comparative advantage.
4.According to Staffan Linder, the factor-endowment theory is useful in explaining trade patterns in manufactured goods, but not primary products.
5.The theory of overlapping demands asserts that trade in manufactured goods is stronger the less similar the demand structures of two countries.
1.True
2.True
3.True
4.False
5.False
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is an example of negative nonverbal behavior?
A. A firm handshake B. Gesturing with open hand C. Maintaining eye contact D. Pointing a finger
The value-to-book ratio reflects an analyst's expectation of the firm's ____________________ value to book value
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
A classified balance sheet differs from an unclassified balance sheet in that:
A. A classified balance sheet will include more accounts than an unclassified balance sheet for the same company on the same date. B. A classified balance sheet is not usually provided to outside parties. C. An unclassified balance sheet is never used by large companies. D. A classified balance sheet groups items into the broad categories of asset, liability, and equity. E. A classified balance sheet presents information in a manner that makes it easier to calculate a company's current ratio.
Compass Metal Bearings produces two sizes of metal bearings (sold by the crate)—standard and heavy. The standard bearings require $200 of direct materials per unit (per crate), and the heavy bearings require $245 of direct materials per unit. The operation is mechanized, and there is no direct labor. Previously Compass used a single plantwide allocation rate for manufacturing overhead, which was $1.55 per machine hour. Based on the single rate, gross profit was as follows:
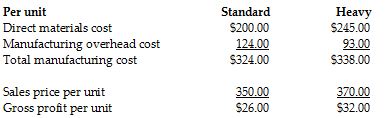
Although the data showed that the heavy bearings were more profitable than the standard bearings, the plant manager knew that the heavy bearings required much more processing in the metal fabrication phase than the standard bearings, and that this factor was not adequately reflected in the single plantwide allocation rate. He suspected that it was distorting the profit data. He suggested adopting an activity-based costing approach.
Working together, the engineers and accountants identified the following three manufacturing activities and broke down the annual overhead costs as shown below:

Engineers believed that metal fabrication costs should be allocated by weight and estimated that the plant processed 12,000 kilos of metal per year. Machine processing costs were correlated to machine hours, and the engineers estimated a total of 380,000 machine hours f