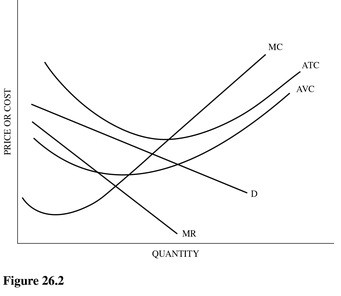
 Refer to Figure 26.2 for a monopolistically competitive firm. At the profit-maximizing output and price, this firm is
Refer to Figure 26.2 for a monopolistically competitive firm. At the profit-maximizing output and price, this firm is
A. Breaking even.
B. Earning an economic profit.
C. Earning a monopoly profit.
D. Earning an economic loss.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Countries such as Brazil, India, and Moldova-well-known sources of organ donors-have banned buying and selling organs. This legal action comes at the risk of driving the trade underground. What idea from Chapter 1 of the text does this story best illustrate?
A. Economic forces always operate despite legal forces. B. Legal and social forces can eliminate economic forces. C. Marginal revenue should equal marginal cost. D. The invisible hand is not always invisible.
Which of the following examples accurately reflects monopolistic competition?
a. Stable, Inc. has a steady number of customers and doesn’t seek any more. b. TopDrawer, Inc. tries to limit its customers to a select few. c. JStar, Inc tries to sell as many cell phones to customers as possible. d. Whole Farms doesn’t really care how many buyers purchase its produce.
A firm announces that it will refund the difference between its price and any price of a competitor that is lower. This is an example of:
A. predatory pricing. B. tying contracting. C. marginal cost pricing. D. a low-price guarantee.
Which of the following statements best describes price flexibility in the economy?
A. Prices tend to be sticky in the short run and stuck in the long run. B. Prices tend to be just as sticky in the short run as in the long run. C. Prices tend to be sticky in the short run but become more flexible over time. D. Prices tend to be flexible in the short run but become more sticky over time.