The difference between pinocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis is that _____
A) pinocytosis brings only water molecules into the cell, but receptor-mediated endocytosis brings in other molecules as well.
B) pinocytosis increases the surface area of the plasma membrane, whereas receptor-mediated endocytosis decreases the plasma membrane surface area.
C) pinocytosis is nonselective in the molecules it brings into the cell, whereas receptor-mediated endocytosis offers more selectivity.
D) pinocytosis can concentrate substances from the extracellular fluid, but receptor-mediated endocytosis cannot.
C
You might also like to view...
Pasteur's experiments proved that
A) Cells cannot survive in swan necked flasks B) In order to grow, cells need to be supplied with oxygen C) Spontaneous generation can only occur if nutrient broth is left open to the environment D) Sterilizing nutrient broth prevents spontaneous generation E) Pre-existing cells present in the air can grow in sterilized nutrient broth
Use the following table to answer the following question(s).Table 1: Cookie parameters with varying fat levels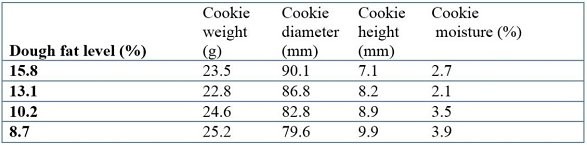 Data from Pareyt, Bram, Faisal Talhaoui, Greet Kerckhofs, Kristof Brijs, Hans Goesaert, Martine Wevers, and Jan A. Delcour, "The Role of Sugar and Fat in Sugar-Snap Cookies: Structural and Textural Properties." Journal of Food Engineering 90, 3 (Feb. 1, 2009): 400-408.Based on the table above, which cookies were the moistest?
Data from Pareyt, Bram, Faisal Talhaoui, Greet Kerckhofs, Kristof Brijs, Hans Goesaert, Martine Wevers, and Jan A. Delcour, "The Role of Sugar and Fat in Sugar-Snap Cookies: Structural and Textural Properties." Journal of Food Engineering 90, 3 (Feb. 1, 2009): 400-408.Based on the table above, which cookies were the moistest?
A. All cookies had the same moisture B. The cookies with the most fat C. The cookies with intermediate amount of fat D. The cookies with the least fat
A shuttle vector is most useful for
A) engineering a complete metabolic pathway. B) identifying the localization of a protein. C) knocking out a gene by cassette displacement. D) making a foreign protein in a mammalian cell.
As fatigue increases, the risk of injury ______.
a. stays the same b. becomes unavoidable c. increases d. decreases