The owner of a perfectly competitive firm that is earning economic losses in the short run
A) should alter the rate of output in order to increase profitability.
B) should cut his own salary in order to reach the break-even point.
C) is actually losing more than he thinks because not all of the implicit costs have been considered.
D) is earning less than he would if he worked for someone else.
D
You might also like to view...
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
1. A utility maximizing person gets marginal utility from consuming their last pencil and pen of 4 and 10 respectively. If pencils cost 10 cents a piece, the pens must cost 25 cents a piece. 2. A utility maximizing person gets marginal utility of 20 from consuming their last piece of bread and of 10 from consuming their last glass of milk. If a piece of bread costs 5 cents, then a glass of milk must cost 20 cents. 3. When a consumer spends all of the income, it must be true that they are maximizing utility.
Market systems are often referred to as "automatic" or "self-regulating" because they function
A) effectively even when no participant in the system plans ahead. B) effectively in the absence of any laws. C) effectively even when the society is breaking down. D) without an overall, comprehensive plan. E) without the intervention of human beings.
When negative externalities exist, a voluntary agreement can be negotiated. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Voluntary agreements usually do not work since the owner has no incentive to negotiate. B) Transactions costs must be low relative to the expected benefits of reaching an agreement. C) Voluntary agreements are difficult to negotiate because they usually involve government intervention. D) Voluntary agreements always leave the owner worse off.
Refer to the table below. If the world price of the product is $6, then Country Y will:
Use the following table to answer the question below for Country Y. Column 1 is the price of a product. Column 2 is the quantity demanded domestically (Qdd) and Column 3 is the quantity supplied domestically (Qsd).
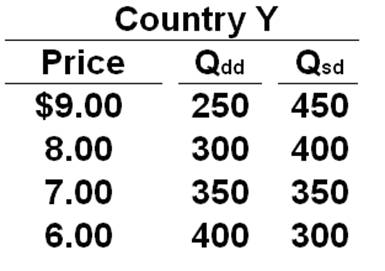
A. Export 100 units of the product
B. Import 100 units of the product
C. Exports of 300 units of the product
D. Imports of 400 units of the product