Refer to Figure 14.3. To maximize the number of workers hired, the labor union will agree to wage rate:
A) W0.
B) W1.
C) W2.
D) W3.
E) none of the above
B
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. In response to gradually falling inflation, this economy will eventually move from its short-run equilibrium to its long-run equilibrium. Graphically, this would be seen as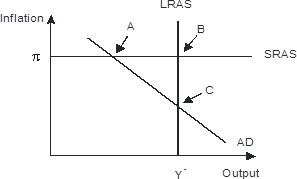
A. long-run aggregate supply shifting leftward B. Short-run aggregate supply shifting downward C. Aggregate demand shifting rightward D. Aggregate demand shifting leftward
In the above figure, if the economy is initially at an equilibrium output at point A and the interest rate is r1, then an open market purchase of bonds by the Fed will
A) not have any impact on short- or long-run equilibrium real Gross Domestic Product (GDP). B) cause interest rates to decline to r2, investment to decline, and aggregate demand to shift inward to the left. C) cause interest rates to increase and output to decline. D) cause interest rates to decline to r2, investment to increase to I2, and the AD curve to shift upward to the right.
Using the data in the above table, the average fixed cost of producing 16 units is
A) $1.11 a unit. B) $1.25 a unit. C) $1.54 a unit. D) $2.22 a unit.
Diminishing marginal utility means that: a. marginal utility is maximized when consumers get the same amount of total utility from every good they consume. b. beyond some point, added units of a product provide lower and lower amounts of marginal utility
c. a consumer would get more utility from the last unit of a good consumed when that good costs $3 than when it costs $1. d. both (b) and (c) are true.