Price controls often generate
A. greater price flexibility.
B. rapid adjustment to market-clearing prices.
C. more efficient markets.
D. black markets.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Real investment spending is ____ real personal consumption.
A. equal to B. greater than C. stable compared to D. highly volatile compared to
A young chef is considering opening his own sushi bar. To do so, he would have to quit his current job, which pays $20,000 a year, and take over a storage building that he owns and currently rents to his brother for $6,000 a year. His expenses at the sushi bar would be $50,000 for food and $2,000 for gas and electricity. The chef's implicit costs are equal to _____.
a. ?$26,000 b. ?$52,000 c. ?$66,000 d. ?$78,000 e. ?$72,000
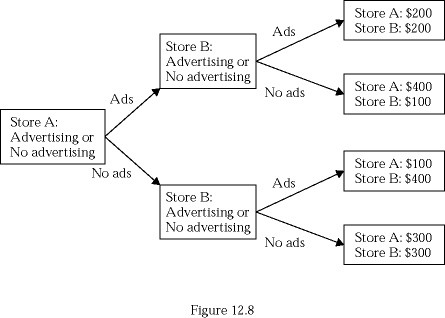 Consider the game tree in Figure 12.8. If both stores' payoffs in the bottom rectangle were $250 instead of $300, the outcome of the game will be that:
Consider the game tree in Figure 12.8. If both stores' payoffs in the bottom rectangle were $250 instead of $300, the outcome of the game will be that:
A. both stores choose to advertise. B. both stores choose not to advertise. C. Store A chooses to advertise but Store B chooses not to advertise. D. Store B chooses to advertise but Store A chooses not to advertise.
What would lead an economist to conclude that Theory A is superior to Theory B?
A) Theory A predicts real-world events better than does Theory B. B) The assumptions underlying Theory A are more realistic than are the assumptions underlying Theory B. C) Theory A explains how people think, whereas Theory B only explains what they do. D) Theory A is based on the assumption that an individual typically cannot determine what is in his or her own best interest, whereas Theory B assumes that each person knows what is in his or her own best interest and acts accordingly.