A consulting firm estimates the following quarterly sales forecasting model:Qt = a + bt +cDThe equation is estimated using quarterly data from 2005 I - 2015 III (t = 1,..., 43). The variable D is a dummy variable for the second quarter where: D = 1 in the second quarter, and 0 otherwise. The results of the estimation are: 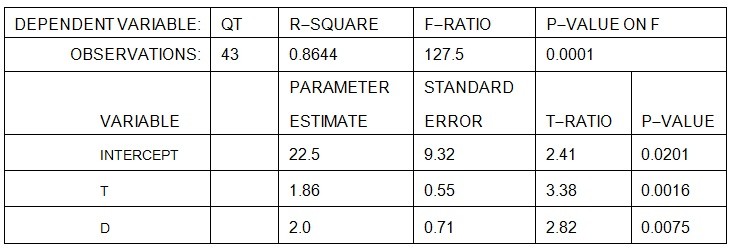 Given the above, these estimates indicate that the second quarter change in sales is
Given the above, these estimates indicate that the second quarter change in sales is
A. 24.5 units higher in the second quarter than in the other three quarters.
B. 1.86 units higher in the second quarter than in the other three quarters.
C. 2.00 units higher in the second quarter than in the other three quarters.
D. 22.5 units higher in the second quarter than in the other three quarters.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Why is plowback the overwhelming favorite among choices of sources of funds for financing corporate investment?
What will be an ideal response?
If purchasing-power parity between France and the U.S. holds, but then U.S. prices rise,
a. the real exchange rate is above its purchasing-power parity value. An increase in the nominal exchange rate can move it back. b. the real exchange rate is above its purchasing-power parity value. A decrease in the nominal exchange rate can move it back. c. the real exchange rate is below its purchasing-power parity value. An increase in the nominal exchange rate can move it back. d. the real exchange rate is below its purchasing-power parity value. A decrease in the nominal exchange rate can move it back.
What is the value of the intra-industry trade index for an industry in which exports are $200 million and imports are $20 million?
a. 2.00 b. (200 + 20)/20 = 11.00 c. 20/[1/2 × (200 + 20)] = 0.18 d. (200 - 20)/200 = 0.90
Economic theory provides a basis for which variables are relevant and should be included in an econometric model. But econometrics provides tools to estimate ____ which tells us ____.
a. a model; the functional form that should be used b. causality; why it happens that way c. a parameter; how much or to what degree things change d. variables; the probability of a specific outcome