Given the indifference curves for an individual as shown below, if the price of good Y = $1, it can be determined that two points on his or her demand curve for good X are:
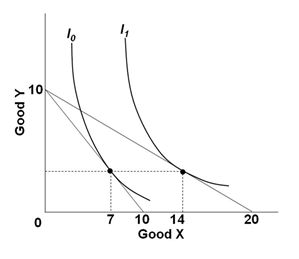
A. (PX = $1, QdX = 10); (PX = $2, QdX = 14)
B. (PX = $1, QdX = 7); (PX = $.50, QdX = 14)
C. (PX = $.50, QdX = 7); (PX = $1, QdX = 10)
D. (PX = $2, QdX = 20); (PX = $1, QdX = 10)
B. (PX = $1, QdX = 7); (PX = $.50, QdX = 14)
You might also like to view...
An increase in the level of prices of goods and services will do what to the long-run aggregate supply curve?
A) not shift the curve at all B) depends upon the long-run aggregate demand curve C) shift it to the right D) shift it to the left
A recession with inflation is know by what term?
If equilibrium GDP is $1 trillion greater than full employment GDP, and there is an inflationary gap of $250 billion, the multiplier is
A. zero. B. 1. C. 2.5. D. 4.
A perfectly inelastic demand is one in which the:
A. response to a change in price is immediate. B. demand curve is perfectly vertical. C. measured elasticity is exactly -1. D. demand curve is perfectly horizontal.