The primary reason that very large nuclei are unstable is due to
A) the cumulative repulsive force of the protons.
B) the cumulative attractive force between the protons and the orbiting electrons.
C) the repulsive force between the neutrons and the protons.
D) the extreme weakness of the gravitational attraction of the protons.
A
You might also like to view...
When and where did the Library of Alexandria exist?
A) from A.D. 600 to A.D. 1800 in Greece B) from A.D. 600 to A.D. 1800 in Egypt C) from 300 B.C. to A.D. 400 in Rome D) from 300 B.C. to A.D. 400 in Greece E) from 300 B.C. to A.D. 400 in Egypt
An object 3.4 mm tall is placed 25 cm from the vertex of a convex spherical mirror. The radius of curvature of the mirror has a magnitude of 52 cm
(a) How far is the image from the vertex of the mirror? (b) What is the height of the image? What will be an ideal response?
Figure R5.10 shows a two-observer space time diagram for an Other Frame that moves at a speed of 0.5 relative to the Home Frame. What are the coordinates of event Q in the Other Frame?
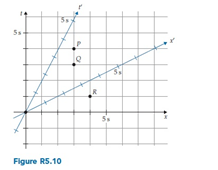
A. t ? = x ? = 5.2 s
B. t ? = x ? = 3.2 s
C. t ? = x ? = 2.6 s
D. t ? = x ? = 1.7 s
E. Other (specify)
Charge of uniform density (20 nC/m2) is distributed over a cylindrical surface (radius = 1.0 cm), and a second coaxial surface (radius = 3.0 cm) carries a uniform charge density of ?12 nC/m2. Determine the magnitude of the electric field at a point 2.0 cm from the symmetry axis of the two surfaces.
A. 2.3 kN/C B. 1.1 kN/C C. 1.7 kN/C D. 3.4 kN/C E. 4.5 kN/C