A production possibilities curve is plotted for a nation producing cotton and jute. Which of the following will cause a parallel rightward shift of the production possibilities curve?
A) An invention of a new fertilizer that increases cotton production by ten percent, without any effect on jute production
B) An invention of a new fertilizer that increases jute production by five percent, without any effect on cotton production
C) An invention of a new fertilizer that increases production of both cotton and jute by ten percent
D) A two-times increase in the price of all cotton products and a three-times increase in the price of all jute products
C
You might also like to view...
Fred's Widget Company has purchased $500,000 in equipment, which can be sold for a salvage value of $300,000 at any time. The best interest rate on alternative investments is 5%
What is the cost of using this machinery for one year? How would your answer be different if the machinery had not yet been purchased?
Refer to the table below. If the profit for each unit of paper product is $2 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $5, what is Big Oaks' marginal cost of producing between points D and E on their production possibilities frontier?
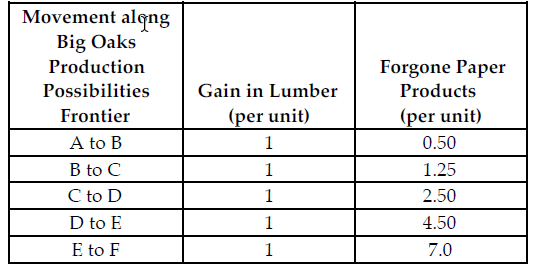
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amount of paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable proportions. The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
A) $22.50
B) $4.50
C) $9
D) $10.50
With respect to monopolies, deadweight loss refers to the
A) socially unproductive amounts of money spent to obtain or acquire a monopoly. B) net loss in consumer and producer surplus due to a monopolist's pricing strategy/policy. C) lost consumer surplus from monopolistic pricing. D) none of the above
An individual with a diversified stock portfolio usually
a. holds only the stocks of conglomerates (firms that participate in many industries). b. deals with several brokerage houses. c. holds stock in several types of firms. d. holds stocks with several maturity dates.