Which is the BEST description of what causes tides?
a. Tides are caused by the Moon's gravitational pull on the Earth.
b. Tides are caused by earthquakes.
c. Tides are caused by the rotation of the Earth.
d. Tides are caused by the gravitational pull of the Earth-Moon system.
e. Tides are caused by the Earth's gravitational pull on the Moon.
d
You might also like to view...
A double-pipe heat exchanger is used to condense steam at 7370 N/m2. Water at an average bulk temperature of 10?C flows at 3.0 m/s through the inner pipe, which is made of copper and has a 2.54-cm-ID and a 3.05-cm-OD. Steam at its saturation temperature flows in the annulus formed between the outer surface of the inner pipe and an outer pipe of 5.08-cm-ID. The average heat transfer coefficient of the condensing steam is 5700 W/(m2 K), and the thermal resistance of a surface scale on the outer surface of the copper pipe is 0.000118 (m2 K)/W.
(a) Determine the overall heat transfer coefficient between the steam and the water based on the outer area of the copper pipe and sketch the thermal circuit.
(b) Evaluate the temperature at the inner surface of the pipe.
(c) Estimate the length required to condense 45 gm/s of steam. (d) Determine the water inlet and outlet temperatures.
GIVEN
ASSUMPTIONS
Steady-state.
Constant steam temperature during condensation.
The flow is fully developed, and copper tube is made of pure copper.
SKETCH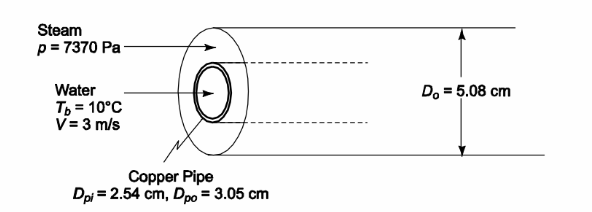
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for steam at 7370 N/m2, the saturation temperature Ts = 40?C, and the heat of vaporization, hfg = 2406 kJ/kg.
The source of electrons in a simple electric circuit is
A) the voltage source. B) energy stored in the voltage source. C) energy released by the voltage source. D) the electrical circuit itself. E) none of the above
A 51.8-kg bungee jumper jumps off a bridge and undergoes simple harmonic motion. If the period of oscillation is 11.2 s, what is the spring constant of the bungee cord?
A) 16.3 N/m B) 19.6 N/m C) 26.1 N/m
The internal resistances of an ideal voltmeter and an ideal ammeter are respectively (ideal meaning the behavior of the system is not changed when using the meter):
a. zero and zero. b. infinite and infinite. c. zero and infinite. d. infinite and zero.