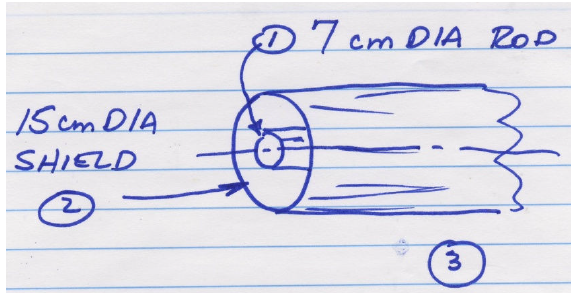
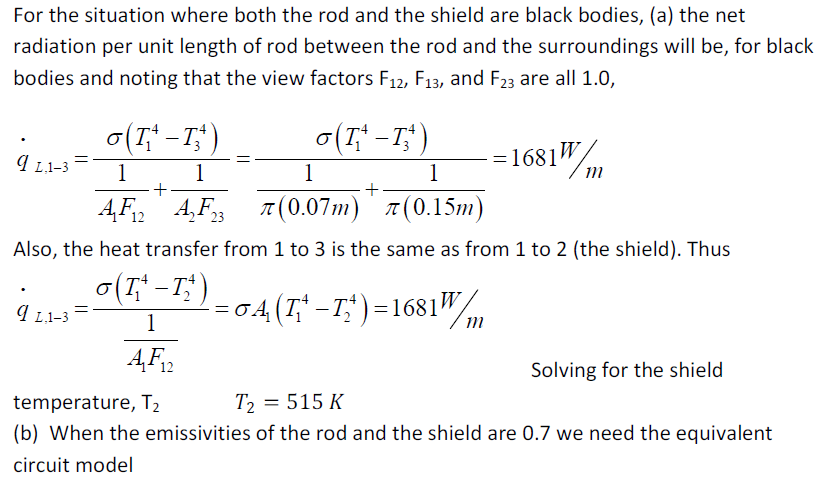
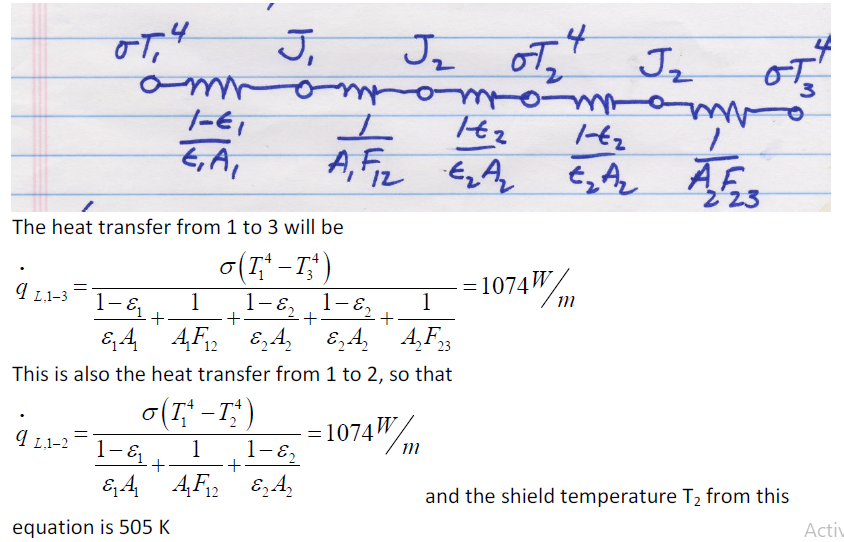
A 7 cm diameter heat exchanger rod at 400ºC is surrounded by a 15 cm diameter heat shield. If the surroundings are a black body at 20ºC, determine the equilibrium temperature of the shield if (a) both rod and shield are black bodies, (b) emissivity of both is 0.7, and (c) the rod is a black body and the shield has emissivity of 0.7.

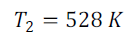
You might also like to view...
Suppose that the star Betelgeuse (the upper left shoulder of Orion) were to supernova tomorrow (as seen here on Earth). What would it look like to the naked eye?
A) Betelgeuse would remain a dot of light but would suddenly become so bright that for a few weeks we'd be able to see this dot in the daytime. B) We'd see a cloud of gas expanding away from the position where Betelgeuse used to be. Over a period of a few weeks, this cloud would fill our entire sky. C) Because the supernova destroys the star, Betelgeuse would suddenly disappear from view. D) Betelgeuse would suddenly appear to grow larger in size, soon reaching the size of the full Moon. It would also be about as bright as the full Moon.
The chief erosive agent now on the Moon is:
A) lunar ice melting and refreezing in the polar regions. B) lava flows welling up in the mare. C) volcanic vents in the rugged highlands. D) the rain of micrometeorites chewing up the regolith. E) rain from cometary debris melting as it enters the Moon's atmosphere.
What is the energy, in eV, of a photon of wavelength 550. nm?
What will be an ideal response?
If the Earth's mass were suddenly made larger but the Moon's mass stayed the same,
a. the Earth would exert a larger force on the Moon. b. the Moon would exert a larger force on the Earth. c. the Earth would exert a larger force on the Moon but the Moon would exert the same force on the Earth as before. d. none of the above