In the context of labor markets, shirking refers to:
A. the nonmonetary disadvantages of certain jobs.
B. the neglecting or evading of work.
C. the elimination of monitoring costs.
D. any scheme where pay is directly related to worker output.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Employers and workers in the protected industry know that the consequences of protection are principally:
a. lower prices for their output, lower profits for owners, and lower wages for workers. b. higher prices for their output, lower profits for owners, and lower wages for workers. c. higher prices for their output, lower profits for owners, and higher wages for workers. d. lower prices for their output, higher profits for owners, and higher wages for workers. e. higher prices for their output, higher profits for owners, and higher wages for workers.
Select whether the statement is true or false.
Macroeconomics and microeconomics are concerned with the well-being of only people with jobs and high incomes; they just examine it from a different perspective. A. True *B. False
Which of the following is an example of a black market activity?
a. Purchasing banned drugs from an individual in a vacant lot b. Purchasing drugs from a pharmacy c. Purchasing automobiles from an authorized dealer d. Purchasing stocks and bonds
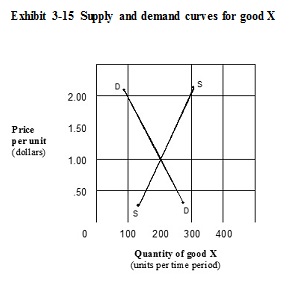
A. no change, because an equilibrium already exists. B. the price to fall below $1.50 and both the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded to fall. C. the price to remain the same, but the supply curve to shift to the left. D. the price to fall below $1.50, the quantity supplied to fall, and the quantity demanded to rise.