Particle A (mass = m, charge = Q) and B (mass = m, charge = 5 Q) are released from rest with the distance between them equal to 1.0 m. If Q = 12 mC, what is the kinetic energy of particle B at the instant when the particles are 3.0 m apart?
a. 8.6 J
b. 3.8 J
c. 6.0 J
d. 2.2 J
e. 4.3 J
D
You might also like to view...
The reason that most extrasolar planets are found close to their parent stars is
A) the planets reflect more light the closer they are to the star. B) more of the starlight is blocked by the planet when it transits the star. C) the amount and frequency of the star's motion are both higher. D) the closer to a star, the hotter and therefore brighter the planet is. E) planets that are close to a star are heated up and therefore larger.
Friction: The figure shows a system consisting of three blocks, a light frictionless pulley, and light connecting ropes that act horizontally on the upper two blocks. The 9.0-kg block is on a perfectly smooth horizontal table. The surfaces of the 12-kg block are rough, with µk = 0.30 between the 12-kg and 9.0-kg blocks. The mass M of the hanging block is set so that it descends at a constant velocity of 3.25 m/s.(a) What is the mass M of the hanging block?(b) The mass M is now changed to 5.0 kg, causing it to accelerate downward after it is released. What is the acceleration of the hanging mass?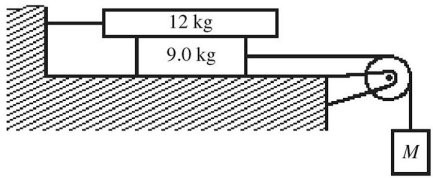
What will be an ideal response?
Write 0.000852 in standard powers-of-10 notation
How long can a four-solar-mass star live?
a. 1 solar lifetime b. 0.03125 solar lifetimes c. 3 solar lifetimes d. None of the other choices are correct.