Besides the obvious fact that chemical mutagens are dangerous to handle, another major disadvantage to their use is that __________
A) most of these mutations are immediately lethal
B) most chemically induced changes are detectable only by sequencing
C) chemical mutagens activate transposons
D) two or more generations of further matings are required to isolate them
E) they alter all A-T and C-G base pairing
B
You might also like to view...
You begin an experiment with two populations of E. coli that are each composed of 100 cells. The cells are all genetically identical (i.e., they are clones). You grow them up in flasks on a lab bench under identical conditions with unlimited resources
After 10,000 generations, you analyze the genome of each population. Do you expect the genomes of each population to be identical after 10,000 generations? A. Yes, because the starting populations were genetically identical. B. Yes, because resources were unlimited. C. No, because mutations will accumulate independently in each population. D. No, because natural selection was not a factor at any point in this experiment. E. No, because mutation and natural selection (once genetic variation is present) were factors in this experiment.
At Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, allele frequencies
A. change from one generation to the next so evolution does not occur. B. change from one generation to the next so evolution occurs. C. None of the answers are correct. D. remain constant from one generation to the next so evolution does not occur. E. remain constant from one generation to the next so evolution occurs.
Following a very large meal that was loaded with carbohydrates, how does the human body to respond to the excess sugars being absorbed into the bloodstream?
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to the accompanying figure in terms of a marine environment. What is the function of the structure labeled as A?
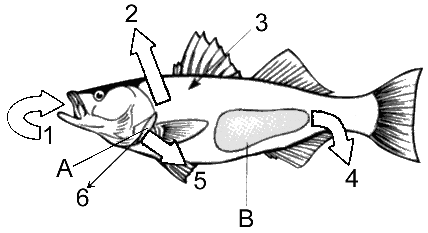
a. salt excretion
b. water gain by osmosis
c. drinking
d. removal of salts and nitrogenous wastes from the blood
e. release of nitrogenous wastes