Compare the problems in achieving growth in an advanced nation with those of a developing nation. Do these problems differ in degree or in kind? Explain.
What will be an ideal response?
The problems differ in kind, but also in degree. The basic problem of the poor countries is poverty itself. They have little ability or incentive to save, and therefore there is little available for investment in physical or human capital. Lack of either form of investment inhibits change and the cycle of poverty continues.
Achieving higher growth rates in advanced nations also requires more investment in both human and physical capital in order to raise productivity. But the requirement is for an expansion of investment, not for an entire transformation of society from the vicious circle of poverty.
You might also like to view...
The process by which union and management representatives negotiate a mutually agreeable contract specifying wages, benefits, and working conditions is called
a. collective bargaining b. mediation c. arbitration d. striking e. litigation
An increase in the U.S. demand for foreign exchange will
a. decrease the price of foreign exchange b. decrease the value of the U.S. dollar c. increase the value of the U.S. dollar d. make foreign goods less expensive in U.S. dollars e. make U.S. goods more expensive in foreign exchange
If most immigrants have relatively low skills, how would the wage for low-skilled labor be affected by a reduction in immigration?
a. The equilibrium wage for low-skill labor would rise. b. The equilibrium wage for low-skill labor would fall. c. The minimum wage for low-skill labor would decrease. d. The earnings gap between low- and high-skill labor would widen.
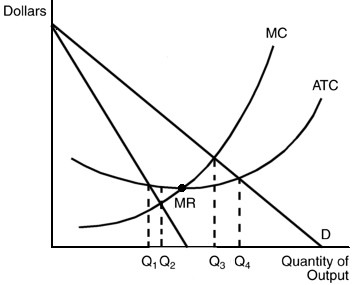 In the above figure, which of the following statements is FALSE if the firm is operating at output level Q2?
In the above figure, which of the following statements is FALSE if the firm is operating at output level Q2?
A. Average costs would be lowered by expanding output. B. Economic profits are positive. C. The price is lower than at an equivalent firm forced by regulators to charge ATC pricing. D. The output is equivalent to an unregulated monopolist.