A rigid, nonconducting tank with a volume of 4 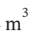 is divided into two unequal parts by a thin membrane. One side of the membrane, representing 1/3 of the tank, contains nitrogen gas at 6 bar and 100°C, and the other side, representing 2/3 of the tank, is evacuated. The membrane ruptures and the gas fills the tank.
is divided into two unequal parts by a thin membrane. One side of the membrane, representing 1/3 of the tank, contains nitrogen gas at 6 bar and 100°C, and the other side, representing 2/3 of the tank, is evacuated. The membrane ruptures and the gas fills the tank.
(a) What is the final temperature of the gas? How much work is done? Is the process reversible?
(b) Describe a reversible process by which the gas can be returned to its initial state. How much work is done?
Assume nitrogen is an ideal gas for which 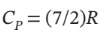 and
and 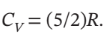
a. In the initial state, the gas has a volume of 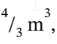 a pressure of 6 bar (600000 Pa) and a temperature of 100 oC (373.15 K). Taking the system to be the entire contents of the tank, the total internal energy of the system is just the internal energy of the part that has the gas in it. The internal energy in the evacuated part is, by definition, zero. It is empty space. Since the tank is nonconducting (insulating) and rigid (constant volume) no heat or work flows enter or leave the tank. Thus, the internal energy in the final state, when the gas has expanded to a volume of 4
a pressure of 6 bar (600000 Pa) and a temperature of 100 oC (373.15 K). Taking the system to be the entire contents of the tank, the total internal energy of the system is just the internal energy of the part that has the gas in it. The internal energy in the evacuated part is, by definition, zero. It is empty space. Since the tank is nonconducting (insulating) and rigid (constant volume) no heat or work flows enter or leave the tank. Thus, the internal energy in the final state, when the gas has expanded to a volume of 4 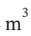 is the same as before the expansion. We can write the first law for the contents of the tank before and after the expansion as
is the same as before the expansion. We can write the first law for the contents of the tank before and after the expansion as
?U = Q + W = 0. For an ideal gas, the internal energy is only a function of temperature.
Therefore, if the internal energy does not change, the temperature of the gas does not change. The final temperature is 100oC. No work is done.
The process is irreversible. The gas expands across a finite pressure difference. Intuitively, this is obvious if one tries to imagine the reverse process, in which the gas all spontaneously flows into 1/3 of the tank.
b. One process to return the gas to its initial state would be reversible isothermal compression, from 4 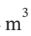 and 6 bar. For isothermal compression,
and 6 bar. For isothermal compression, 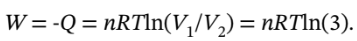 Since nRT is
Since nRT is
equal to PV and is constant, we have W = -Q = 4 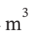 * 200000 Pa * ln(3) = 878900 Pa
* 200000 Pa * ln(3) = 878900 Pa 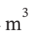 = 878900 J.
= 878900 J.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following treatment methods is used to control acidity?
a. softeners b. neutralizing tanks c. activated charcoal filters d. manganese oxidizing filters
An automatic transmission has a whine in park and neutral, noisier when cold. What could be the cause?
A) A worn final drive bearing B) Loose planetary needle bearings C) A badly worn pump D) Loose pump drive chain
Why is the thermal conductivity of superinsulation orders of magnitude lower than the thermal conductivity of ordinary insulation?
What will be an ideal response?
A given weight of water can carry more heat than the same weight of air because _____
a. water is heavier than air b. water has a greater specific heat c. air has a greater pressure drop d. water has less friction within piping