A decrease in demand and an increase in supply results in a(n)
a. decrease in equilibrium price and an ambiguous effect on equilibrium quantity
b. increase in equilibrium price and an ambiguous effect on equilibrium quantity
c. ambiguous effect on equilibrium price and an increase in equilibrium quantity
d. ambiguous effect on equilibrium price and an decrease in equilibrium quantity
e. increase in equilibrium price and a decrease in equilibrium quantity
A
You might also like to view...
The primary reason why monopolistically competitive firms cannot earn an economic profit in the long run is because
A) there are barriers to entry. B) there is freedom of entry. C) the antitrust laws prevent profit from increasing. D) recessions occur. E) they collude to earn a normal profit.
If the Canadian dollar depreciates, holding other things constant, it makes Canadian imports
a. More expensive for Canadian customers b. Less expensive for Canadian customers c. Neither more or less expensive for importers d. None of the above
The Taylor rule accurately predicted the changes in the federal funds target during the period
A) when Alan Greenspan was the chairman of the Federal Reserve Board. B) when Paul Volcker was the chairman of the Federal Reserve Board. C) when Arthur Burns was the chairman of the Federal Reserve Board. D) when William McChesney Martin was the chairman of the Federal Reserve Board.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 28.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow.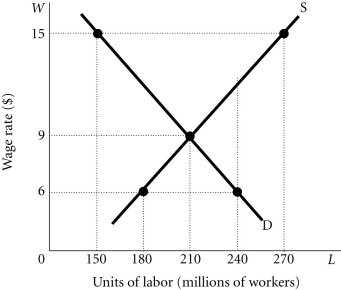 Figure 28.1Refer to Figure 28.1. The equilibrium wage rate is $________ and the equilibrium number of people employed is ________ million people.
Figure 28.1Refer to Figure 28.1. The equilibrium wage rate is $________ and the equilibrium number of people employed is ________ million people.
A. 6; 180 B. 15; 270 C. 15; 150 D. 9; 210