Which variable is likely to undergo the largest change in value resulting from a mutation that introduces a new allele into a population at a locus for which all individuals formerly had been fully homozygous?
A) average heterozygosity
B) nucleotide variability
C) geographic variability
D) average number of loci
A
You might also like to view...
In adult vertebrates, which of these is not one of the four principal kinds of primary tissues?
A. epithelial B. connective C. supportive D. muscle E. nerve
Snow geese usually select mates of their own color, an example of ____
a. genetic drift b. founder effects c. population bottlenecks d. nonrandom mating e. random mating
The abdominal segments of Drosophila have no appendages. Loss of function of bithorax genes results in appendages forming in these abdominal segments. Therefore, __________
A) bithorax mutations are necessarily recessive B) bithorax genes normally activate appendage-forming genes C) ultrabithorax usually acts to oppose bithorax genes D) bithorax normally activates a gene that negatively regulates appendages in the abdomen E) expression of bithorax wild-type genes suppresses all appendage formation
In the accompanying figure, ionic bonds would form between the R groups of which amino acids?
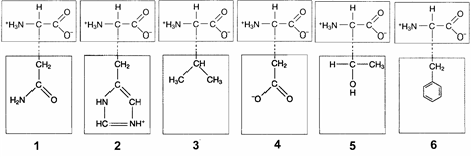
a. 1 and 3
b. 2 and 4
c. 3 and 5
d. 4 and 6
e. 3 and 6