Total consumer surplus in a market is measured as the
A. area bounded below the market clearing price and above the market supply curve.
B. horizontal distance from the vertical (price) axis to the equilibrium quantity.
C. vertical distance from the horizontal (quantity) axis to the market clearing price.
D. area bounded above the market clearing price and beneath the market demand curve.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Often you will hear students say that a college degree is nothing more than a piece of paper
They argue that there are many successful people who don't go to college that are managing large corporations or otherwise have fulfilling and rewarding careers. Given that this is true does this undermine the usefulness of a college degree as a signaling device?
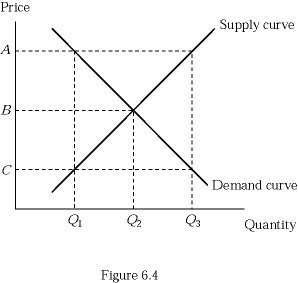 Refer to Figure 6.4. Suppose that the market is currently in equilibrium and the government decides to impose a minimum price equal to price C in the graph. How will the equilibrium quantity and price change as a result of the price floor?
Refer to Figure 6.4. Suppose that the market is currently in equilibrium and the government decides to impose a minimum price equal to price C in the graph. How will the equilibrium quantity and price change as a result of the price floor?
A. It won't. The price floor is above the equilibrium, so the market stays at equilibrium. B. It will cause a shortage because at the price floor, the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied. C. It will cause a surplus because at the price floor, the quantity demanded is below the quantity supplied. D. It won't. The price floor is below the equilibrium, so the market stays at equilibrium.
The sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is equal to
A) the deadweight loss. B) the economic surplus. C) zero. D) total profit.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 15.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 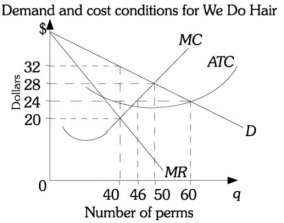 Figure 15.2 Refer to Figure 15.2. If We Do Hair is maximizing profit as a monopolistically competitive firm, its total costs are
Figure 15.2 Refer to Figure 15.2. If We Do Hair is maximizing profit as a monopolistically competitive firm, its total costs are
A. $1,200. B. $960. C. $800. D. $660.