Calculate Q, W, 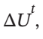 and
and 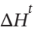 for each of these processes, and sketch the paths of all processes on a single PV diagram.
for each of these processes, and sketch the paths of all processes on a single PV diagram.
The state of an ideal gas with 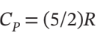 is changed from P = 1 bar and
is changed from P = 1 bar and 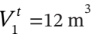 to
to 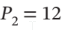 bar and
bar and 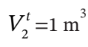 by the following mechanically reversible processes:
by the following mechanically reversible processes:
(a) Isothermal compression.
(b) Adiabatic compression followed by cooling at constant pressure.
(c) Adiabatic compression followed by cooling at constant volume.
(d) Heating at constant volume followed by cooling at constant pressure.
(e) Cooling at constant pressure followed by heating at constant volume.
For all parts of the problem, the final temperature is the same as the initial temperature (we know this because the final PV is equal to the initial PV, and because one of the paths is specified to be isothermal). So, for all of the paths, ?H = ?U = 0. Furthermore, because for any path, ?U = Q + W, for each of the paths we have Q = - W. So, for each path, we just have to compute W (or Q) and we are done.
a. For isothermal compression,
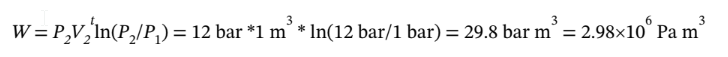
W = 2980 kJ
Q = -W = -2980 kJ
b. For the adiabatic compression to the final pressure and some intermediate volume that we'll call 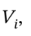 we have
we have
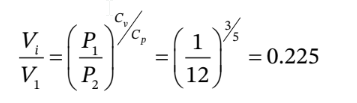
so the intermediate volume is 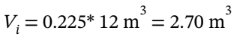
The work for an adiabatic process on an ideal gas (with constant heat capacity) can be written as
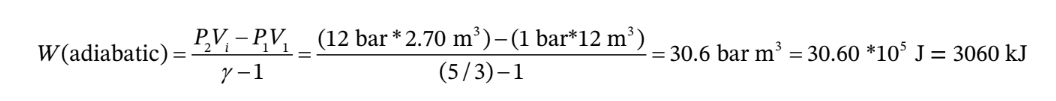
The work for the cooling at constant pressure to the final volume of  is just
is just
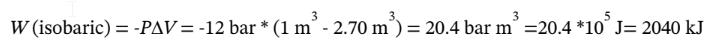
The total work is therefore W = 3060 kJ+2040 kJ = 5100 kJ, and Q = -5100 kJ
c. For adiabatic compression to the final volume and some intermediate pressure that we'll call 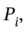 we have
we have
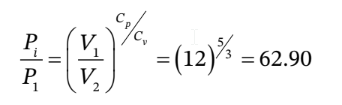
So, the intermediate pressure is 1 bar * 62.90 = 62.90 bar
The work for the adiabatic step is then
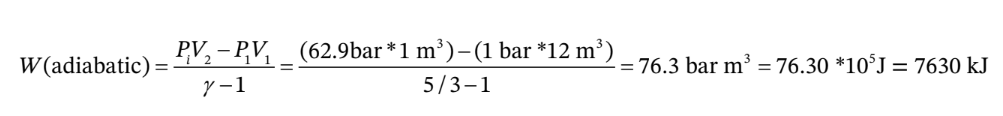
No work is done in the constant volume step, so the total work is W = 7630 kJ, and Q = -7630 kJ
d. No work is done during the heating at constant volume to the final pressure of 12 bar. The work done during the subsequent cooling at constant pressure is just
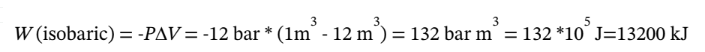
So, the total work is W = 13200 kJ, and Q = -13200 kJ
e. When the gas is cooled at constant pressure, the work done is
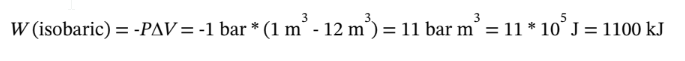
No work is done during the subsequent heating at constant volume, so the total work is
W = 1100 kJ, and Q = -1100 kJ
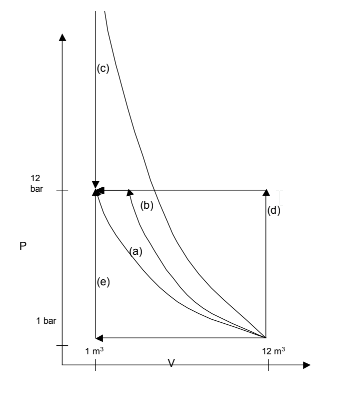
The various paths are sketched on the following PV diagram:
You might also like to view...
Which of the following are challenges facing managers today?
a. empowerment b. diversity c. productivity d. ethics e. All of these are challenges facing managers today.
Training in blueprint reading includes developing the ability to ____ the various manufacturing and fabricating processes required to make a part.
A. separate B. delegate C. synthesize D. visualize
Why did the Janissaries depose Ottoman Sultan Mustafa II in 1703?
a. They disapproved of his signing of a peace treaty with the Habsburgs. b. They sought to replace him with a weaker successor. c. They sought more independence and power for themselves. d. They were weary of war with the Habsburgs.
When maintaining hard and soft surface flooring in a sustainable way ___________
A. carpets should be shampooed frequently and floors should be cleaned and waxed often B. use information provided by the Carpet and Rug Institute, US EPA, and Green Seal C. Both A and B D. none of the above