In general, does the demand for labor become more or less elastic as we increase the number of other variable inputs used in a production process?
A) More elastic
B) No change in elasticity
C) Less elastic
D) We cannot answer this question without more information about the other inputs
A
You might also like to view...
George makes $250 a week working as a student aid. When he cashes his check he takes $100 to the cashiers office to pay part of his tuition. $25 goes to paying off his books, $75 goes for entertainment and $50 he keeps for unexpected expenditures
Which of the following statements is TRUE? A) The transactions demand for money is $125, the precautionary demand is $75 and the asset demand is $50. B) The transactions demand for money is $0, the precautionary demand is $250 and the asset demand is $0. C) The transactions demand for money is $200, the precautionary demand is $50 and the asset demand is $0. D) The transactions demand for money is $250, the precautionary demand is $0 and the asset demand is $0.
If a monopoly is operating on the demand curve where price elasticity is equal to -3, and MR equals 2, then price is equal to
A) 3. B) 2. C) 1. D) 0.
Supply can shift due to changes in price
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
In the figure below, AB is the production-possibility curve of Canada. The line PQ shows the price ratio of one bushel of wheat/bale of cotton. I1 and I2 are two of the community indifference curves of Canada. With free trade, Canada can achieve a level of well-being corresponding to I2. In the absence of international trade, one bushel of wheat will exchange for ________ bale(s) of cotton in Canada. After Canada engages in international trade, one bushel of wheat will exchange for ________ bale(s) of cotton.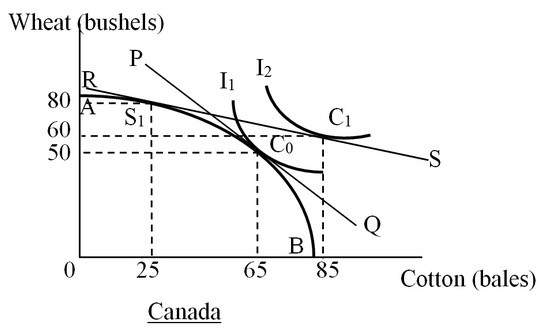
A. 65, 85 B. four; one C. one; 0.25 D. one; four