In order to conserve energy, the inner surface of double-glazed windows are treated with a low emissivity coating that reduces the emissivity of the uncoated surface from 0.95 to 0.5 for the coated surface. If the temperatures of the two glass panes are 20°C and 0°C, respectively, determine the reduction in heat transfer in a coated double-glazed window as compared with the uncoated one.
GIVEN
• Double glazed windows treated with low emissivity coating that reduce emissivity of uncoated surface from ?1 =0.95 to ?2= 0.5.
• Temperature of glass pane 1 (T1)= 200C = 293 K
• Temperature of glass plane 2 (T2) = 00C = 273 K
FIND
Reduction in heat transfer in coated double glazed window as compared to uncoated one.
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the Stephan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 × 10–8 W/(m2 K4)
When the double glazed window is not coated heat transfer between the surfaces is
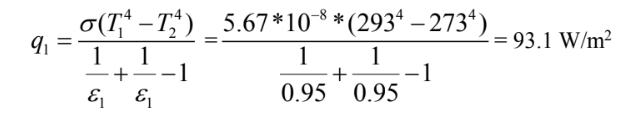
When the double glazed window is coated heat transfer between the surfaces is
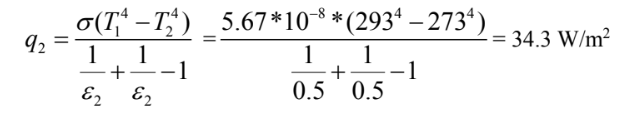
Thus the reduction in heat transfer q= q1-q2 = 58.8 W/m2
You might also like to view...
Transformers: An ideal transformer with 120 turns in its secondary supplies 12 V at 220 mA to a toy train. The primary is connected across a 120-V wall outlet.(a) How many turns are in the primary?(b) What is the primary current?(c) What power is delivered by the wall outlet?
What will be an ideal response?
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
Consider an infinite solenoid with a rectangular cross section instead of a circular cross section. 1. The solenoid’s magnetic field must everywhere still point parallel to the solenoid’s central axis. 2. The solenoid’s magnetic field must still be zero everywhere outside the solenoid. 3. The solenoid’s magnetic field in the solenoid’s hollow interior must still have a uniform magnitude ? 0 (NI/L), where N is the number of turns in length L and I is the current carried by each turn
A block and a beaker of water are placed side-by-side on a scale (case A). The block is then placed into the beaker of water, where it floats (case B). How do the two scale readings compare?
1.Scale A reads more than scale B. 2.Scale A reads the same as scale B. 3.Scale A reads less than scale B. 4.Not enough information.
Which of these has a higher frequency than visible light?
A) radio wave B) microwave C) infrared wave D) ultraviolet wave E) all do