The property of money that allows for the settling of debts that mature in the future is
A) store of value. B) liquidity.
C) acceptability. D) standard of deferred payment.
D
You might also like to view...
An economy produces only two goods: paper and scissors. Dyes from paper production pollute a nearby river. Use a production possibilities curve (PPC) to illustrate your explanation of how the unfettered market would fail to provide the efficient mix of paper and scissors.
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following is most likely to create diseconomies of scale?
A) concentration of production in a small number of very large plants. B) the use of automation devices. C) technological advance. D) division of labor.
Assume the table shown is for a hat factory, and shows the total production of hats given various numbers of employees. Adding a third worker increases production:
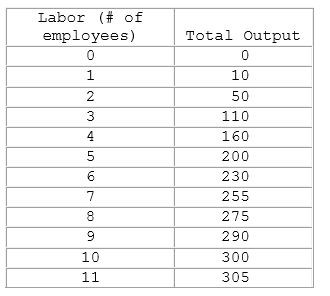
A. by 60 hats.
B. by more than the second worker.
C. to 110 hats.
D. All of these are true.
Suppose there are two factories on a river, and both need clean water for their production processes. The upstream factory takes in clean water and dumps dirty water back into the river. The downstream firm must clean up the water it gets from the river
before using it. In this situation A) the private costs of the downstream factory are more than the private costs of the upstream factory, but for both factories private costs and social costs are the same. B) the social costs are greater than the private costs for the upstream firm, while the social costs are less than the private costs for the downstream firm. C) the upstream factory's private costs are less than its social costs, and its external costs are borne by the downstream factory. D) the internal costs of the upstream factory are externalized by the downstream factory, which then passes them on to its customers.