If a nation starts out with very little capital
A. it is doomed to eternal poverty because it will not be able to divert productive resources from producing consumer goods to producing capital goods.
B. it can quite easily divert some resources from producing consumer goods to producing capital goods.
C. if it possesses a valuable commodity that the industrial world wants such as oil, it can sell its oil in exchange for plant and equipment and thus industrialize.
D. None of the choices are true.
C. if it possesses a valuable commodity that the industrial world wants such as oil, it can sell its oil in exchange for plant and equipment and thus industrialize.
You might also like to view...
Bart operates a lemonade stand in front of his house. His father works at the Springfield Nuclear Power Plant. Which of the following is most likely to be true about the calendar time period associated with the short run for the two industries?
A. The short run would be one year for the lemonade stand and exactly two years for the nuclear plan
B.The short run is longer for the power plant than it is for the lemonade stand
C.The short run is the same for the power plant as it is for the lemonade stand.
D. The short run is shorter for the power plant than it is for the lemonade stand.
The basic principles of economics suggest that
a. markets are seldom, if ever, a good way to organize economic activity. b. government should become involved in markets when trade between countries is involved. c. government should become involved in markets when those markets fail to produce efficient or fair outcomes. d. All of the above are correct.
Regulations that strictly limit pollution
A. provide firms no incentives to reduce pollution once a standard is met. B. provide no incentives for firms to discover loopholes in the regulations. C. tend to be an economically efficient way to reduce pollution. D. has been a simple way for some firms to reduce pollution to zero.
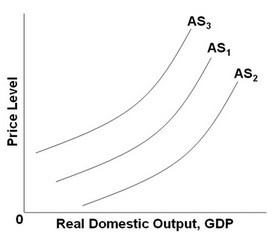 Refer to the above graph. Which factor will shift AS1 to AS3?
Refer to the above graph. Which factor will shift AS1 to AS3?
A. An increase in input prices. B. A decrease in business taxes. C. A decrease in household indebtedness. D. An increase in productivity.