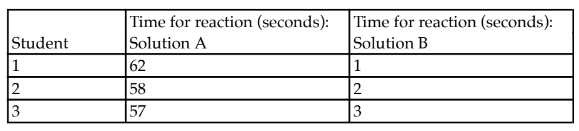
Write the chemical equation for this reaction. Determine average values for each beaker. Explain how the reaction times differed. What may be present in beaker B that is absent from beaker A?
Carbon dioxide and water readily combine to form carbonic acid. The change in pH as the acid dissociates can be demonstrated with an indicator dye that changes color at a particular pH. In your physiology lab, you perform this experiment in two beakers containing room-temperature water and indicator, labeled as A and B. CO2 is bubbled into solutions A and B from a pressurized tank for 10 seconds. A stopwatch was used to measure how long it took for the solutions to change color. The data below were generated by the students.
CO2 + H2O ?H2CO3 ?H++ HCO3-
Average time for beaker A to change is 59 seconds, and for beaker B to change is 2 seconds, that is, the reaction
occurred faster in solution B. For this to occur, an enzyme such as carbonic anhydrase must have been present in beaker B.
You might also like to view...
The anterior pituitary secretes:
a. TSH b. oxytocin c. ADH d. all of the above
If the tidal volume is 500 ml and the anatomic dead space volume is 150 ml, only 350 ml of air enters the alveoli during inspiration
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The capacity of a muscle to respond to an electrical stimulus is ______.
a. elasticity
b. contractility
c. excitability
d. extensibility
Twelve-year old Madeline has not yet experienced a bone growth spurt, meaning she is not yet producing which particular chemicals necessary for this to occur?
A. calcitonin B. sex hormones C. parathyroid hormone D. vitamin D E. growth hormone