In many developing countries, starting a business involves navigating a labyrinth of rules and regulations and red tape. Paying a bribe to expedite paperwork is a common practice
As Samuel Huntington puts it—"the only thing worse than a society with a rigid, overcentralized, dishonest bureaucracy is one with a rigid, overcentralized, honest bureaucracy." The argument is that bribes increase economic activity because, without bribes to grease bureaucrats' palms, starting a business would be an extremely long, drawn-out process and would probably drive investors away. Is this always the case, or does bureaucratic corruption involve other costs? Explain your answer.
Most evidence suggests that bureaucratic corruption actually lowers economic efficiency. Although paying a bribe may ensure that economic activity proceeds smoothly, it is a highly inefficient way of getting things done. The resources that are used to pay bribes could have been utilized toward more productive activities in the economy. Also, citizens interact with government officials and bureaucrats very often. Once bribery becomes endemic in a society, it becomes very difficult to control. This makes bureaucratic corruption even more challenging than political corruption.
A-head: CONTROLLING POLITICIANS
Concept: Bureaucratic corruption
You might also like to view...
The money supply and velocity of money tell us the:
A. price value of real output. B. real output. C. nominal value with inflation accounted for. D. nominal value of firm output.
Exemptions and deductions included in the tax laws
A. Make the tax structure more progressive. B. Reduce horizontal inequities. C. Are designed to encourage specific economic activities. D. Reduce vertical inequities.
If a nation produces more consumer goods and less capital goods, then the nation will have:
A. More consumption now, but less consumption later B. Less consumption now, but more consumption later C. More consumption now, with no effect on consumption later D. Less consumption later, with no effect on consumption now
Use the figure below, which shows a linear demand curve and the associated total revenue curve, to answer the question.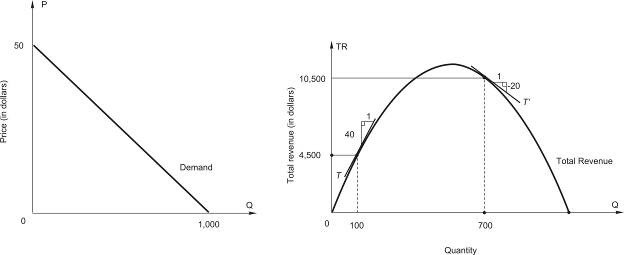 The price at which total revenue is maximized is $________.
The price at which total revenue is maximized is $________.
A. 10 B. 20 C. 30 D. 15 E. 25