The theory of the kinked demand curve is used to explain
a. bizarre corporate behavior.
b. sales maximization.
c. the maximin criterion.
d. sticky prices in oligopolies.
d
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, a decrease in government spending that decreases aggregate demand from AD1 to AD will lead to a short-run equilibrium at__ creating _____gap.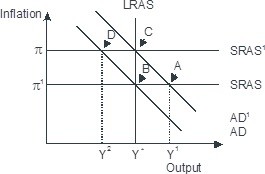
A. B; no output B. D; an expansionary C. B; recessionary D. D; a recessionary
If the government reduces expenditure on goods and services by $30 billion, then aggregate demand
A) increases by $30 billion and real GDP increases. B) decreases by more than $30 billion and real GDP decreases. C) increases by more than $30 billion and real GDP increases. D) decreases by $30 billion and real GDP decreases. E) increases and potential GDP increases.
In the above figure, if the firm increases its output from Q2 to Q3, it will
A) reduce its marginal revenue. B) increase its marginal revenue. C) decrease its profit. D) increase its profit.
In a voluntary contribution game:
A. each member of a group makes a contribution to a common pool which benefits only the contributor, and this leads to alignment of individual and collective interests. B. each member of a group makes a contribution to a common pool which benefits everyone, and this leads to alignment of individual and collective interests. C. each member of a group makes a contribution to a common pool which benefits only the contributor, and this leads to a conflict between individual and collective interests. D. each member of a group makes a contribution to a common pool which benefits everyone, and this leads to a conflict between individual and collective interests.