The portion of a mushroom that you typically eat is
a. the fruiting body.
b. the reproductive structure.
c. the chytrid sac.
d. both the fruiting body and the reproductive structure.
D
You might also like to view...
Humans and chimpanzees last shared a common ancestor around _____ million years ago, and our genomes now differ by about _____%
A. 5-7; 1 B. 5-7; 10 C. 10-20; 1 D. 10-20; 10 E. 20-50; 50
Experimental mutations in the timing of Hox gene expression cause lab mice to develop deformed limbs. This is an example of
A. evolution of a new gene to code for the new morphology. B. homeosis. C. heterochrony. D. a change in spatial pattern of gene expression. Clarify Question · What is the key concept addressed by the question? · What type of thinking is required? · What key words does the question contain and what do they mean? Gather Content · What do you already know about heterochrony? Consider Possibilities · Consider the different answer options. Which can you rule out? Choose Answer · Given what you now know, what information and/or problem solving approach is most likely to produce the correct answer? Reflect on Process · Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
How are these two amino acids attached?
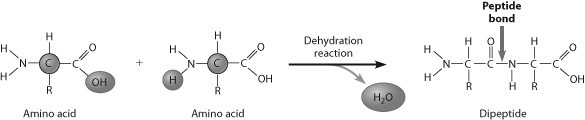
A) amino group to amino group
B) amino group to carboxyl group
C) carboxylic acid group to carboxyl group
D) through a hydrolysis reaction
Papillomaviruses are transmitted by (aerosols/direct contact/secretions)
What will be an ideal response?