When an economy is in an economic boom, discretionary fiscal policy would call for ________, and the automatic stabilizers would ________.
A. lowering tax rates; lower tax revenues
B. lowering tax revenues; lower tax rates
C. increasing tax rates; lower tax revenues
D. increasing tax rates; increase tax revenues
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The figure above shows a perfectly competitive firm. The firm is operating; that is, it has not shut down. The firm produces
A) 20 units of output and makes zero economic profit. B) 20 units of output and incurs an economic loss. C) 10 units of output and makes zero economic profit. D) 10 units of output and incurs an economic loss.
Everything else being constant, a lower real interest rate
A) increases desired saving and net exports. B) decreases desired saving but increases net exports. C) increases desired saving and investment. D) increases desired investment but decreases net exports.
In September 1992, Great Britain changed its exchange rate system. How?
A) It abandoned the gold standard in favor of pegging to the U.S. dollar. B) It joined in with the new euro. C) It switched from an exchange rate peg to floating. D) It abandoned the sterling backing for the British pound.
Refer to the given data, symbols, and assumptions. If migration is costless and unimpeded, the combined value of total product in the two countries will:
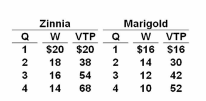
Symbols: Q = number of workers demanded; W = wage rate; and VTP = value of the
cumulative total product (output) of the particular number of workers.
Assumptions: (1) The current wage in Zinnia is $20 and the current wage in Marigold is $12; (2) full employment exists in both countries.
A. decline from $62 to $36.
B. decline from $120 to $70.
C. increase from $36 to $62.
D. increase from $62 to $70.