Why are massive main sequence stars not likely to have planets that contain life?
a. The life zones around these stars is too small.
b. These stars would sweep away all of the material from which planets could form.
c. These stars are too hot to allow water to exist as a liquid on any planets that might form.
d. These stars are on the main sequence for too short a time to allow life to evolve.
e. These stars are almost always binaries and planetary orbits are unstable around binaries.
D
You might also like to view...
Coulomb's Law: Two equal and opposite charges are a small distance apart, forming an electric dipole. A positive charge +q is placed above these charges, as shown in the figure, equidistant from both of them. Which diagram below best gives the direction of the net force the dipole exerts on the charge +q?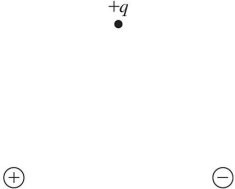
A. ![]()
B. ![]()
C. 
D. 
The gravitational red shift is caused by
A) gravitational lensing. B) rotating black holes. C) time dilation. D) Rayleigh scattering in the atmosphere.
A 1.8-kg block is released from rest at the top of a rough 30° inclined plane. As the block slides down the incline, its acceleration is 3.0 m/s2 down the incline. Determine the magnitude of the force of friction acting on the block
a. 4.2 N b. 3.0 N c. 3.4 N d. 3.8 N e. 2.3 N
A Geiger counter registers a count rate of 8,000 counts per minute from a sample of a radioisotope. The count rate 24 minutes later is 1,000 counts per minute. The half-life of the radioisotope is 8 minutes
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false