Exhibit 16-5 Money, investment and product markets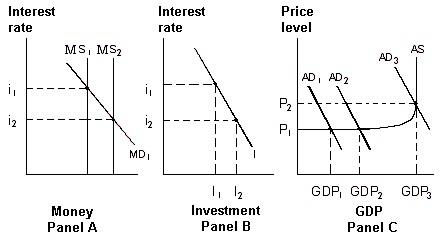
In Exhibit 16-5, a shift in aggregate demand from AD2 to AD3:
A. increases real GDP, and lowers the price level.
B. decreases real GDP, and lowers the price level.
C. increases real GDP, and raises the price level.
D. decreases real GDP, and raises the price level.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Refer to Scenario 1 . If you start the course in such a way that each exam score is worse than your previous average what should happen to your average score?
What would happen to your average if the next exam score was larger than your previous exam score? Explain.
Grant has $200 to spend each month on restaurant meals and jazz performances at his
neighborhood jazz club. The price of a typical restaurant meal is $20 and the price of a jazz performance ticket is $10. Grant is maximizing his utility by consuming 6 restaurant meals and attending 8 jazz performances. Suppose Grant still has $200 to spend, but the price of restaurant meal rises to $25, while the price of jazz performance ticket drops to $8. Can it be determined if Grant is better off or worse off than he was before the price change? Use a budget constraint/indifference curve graph to illustrate your answer.
If a firm must produce a significant share of market output before low average costs can be achieved, the structure of this industry will tend to be
a. monopolistic competition b. perfect competition c. oligopoly d. either monopolistic competition or oligopoly e. either perfect competition or monopolistic competition
The horizontal summation of the demands of each consumer at different price levels is called:
A. speculative demand. B. the market demand curve. C. the price elasticity of market demand. D. consumer surplus.