Starting from very far away, an object is moved closer and closer to a converging lens, eventually reaching the lens. What happens to its image formed by that lens? (There could be more than one correct choice.)
A) The image gets farther and farther from the lens.
B) The image eventually changes from real to virtual.
C) The image eventually changes from virtual to real.
D) The image gets closer and closer to the lens.
E) The image keeps getting larger and larger.
B
You might also like to view...
The potential energy for a certain mass moving in one dimension is given by U(x) = (2.0 J/m3)x3 - (15 J/m2)x2 + (36 J/m)x - 23 J. Find the location(s) where the force on the mass is zero
A) 4.0 m, 5.0 m B) 1.0 m C) 2.0 m, 3.0 m D) 3.0 m, 5.0 m
A brass bar twisted by torques T acting at the ends has the follow- ing properties: L 5 2.1 m, d 5 38 mm, and G 5 41 GPa. The torsional stiffness of the bar is approximately:
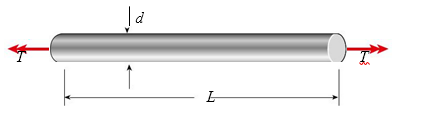
(A) 1200 N?m
(B) 2600 N?m
(C) 4000 N?m
(D) 4800 N?m
Uniform Circular Motion: If a satellite moves with constant speed in a perfectly circular orbit around the earth, what is the direction of the acceleration of the satellite?
A. in the forward direction B. in the backward direction C. outward away from the earth D. inward toward the earth E. The acceleration is zero because the speed is constant.
Simple Harmonic Motion: An air-track cart is attached to a spring and completes one oscillation every 5.67 s in simple harmonic motion. At time t = 0.00 s the cart is released at the position x = +0.250 m. What is the position of the cart when t = 29.6 s?
A. x = 0.0461 m B. x = 0.210 m C. x = 0.218 m D. x = 0.342 m E. x = -0.218 m