Gene A is located near gene B on Chromosome 13 in humans. A mutation in the germ line of an individual with the haplotype AB generates gametes with the genotype Ab
Many descendants of this founder individual carry the b mutation, which predisposes carriers to high blood pressure. Initially, all descendants who inherit the b mutation also inherit the neighboring A allele. Through the generations, fewer and fewer descendants with the b mutation carry the A allele, and instead they have the a allele. (Individuals with A and a are equally healthy and fit.) Explain how the b and A alleles are separated.
Eventually, the b mutation will be separated from the A allele by meiotic recombination. Meiotic recombination exchanges portions of homologous chromosomes, and thereby generates great diversity among the gametes of each individual. The locations of the one to five exchanges per chromosome during meiosis in humans are more or less random. Thus, each passing generation increases the cumulative likelihood of a recombinational crossover between any two neighboring genes (A and b). Such a recombinational crossover in an individual heterozygous for both genes (Ab and aB) will separate two alleles that were originally linked (yielding AB and ab).
You might also like to view...
As you study two closely related predatory insect species, the two-spot and the three-spot avenger beetles, you notice that each species seeks prey at dawn in areas without the other species
However, where their ranges overlap, the two-spot avenger beetle hunts at night and the three-spot hunts in the morning. When you bring them into the laboratory and isolate the two different species, you discover that the offspring of both species are found to be nocturnal. You have discovered an example of _____. A) mutualism B) character displacement C) Batesian mimicry D) facultative commensalism E) resource partitioning
Entropy is the amount of ____ in a system
Any help with this? Thanks.
What happens when a phage containing bacterial DNA attaches to and injects DNA into another bacterial cell?
a. the phage is destroyed b. the phage replicates c. the bacterial cell dies from the phage infection d. the bacterial cell lives and produces many copies of the phage e. the bacterial cell becomes a partial diploid and may undergo genetic recombination
Carbon and hydrogen make up many biologically important molecules. Carbon has an electronegativity of 2.55, whereas hydrogen has an electronegativity of 2.2. Based on the electronegativity difference between the atoms, the carbon and hydrogens shown here have just formed
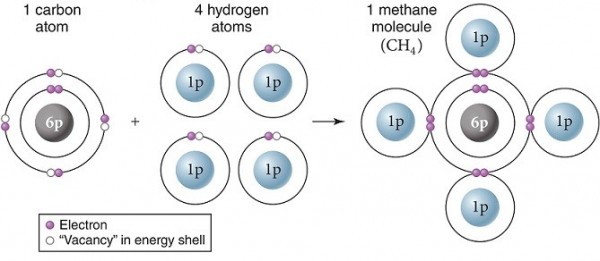
A. an ionic bond.
B. a hydrogen bond.
C. a polar covalent bond.
D. a nonpolar covalent bond.
E. an element.