In Figure 6.1, which area represents a recession? 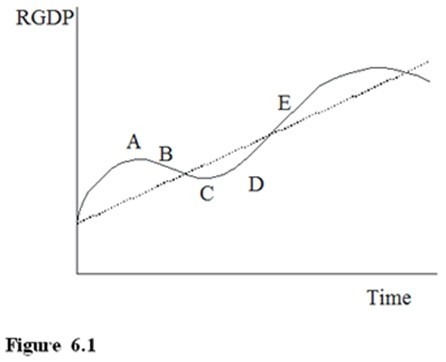
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The economic theory that suggested an alternative to the rising unemployment and inflation that the static Phillips curve analysis could not explain was the:
a. new classical economic theory. b. monetarist economic theory. c. new Keynesian economic theory. d. classical economic theory. e. traditional Keynesian economic theory.
Which of the following best describes an outcome of a stronger exchange rate?
a. A stronger exchange rate makes it easier for exporters to sell their goods abroad while making imports cheaper, so a trade deficit (or a reduced trade surplus) results. b. A stronger exchange rate makes it easier for exporters to sell their goods abroad while making imports cheaper, so a trade surplus (or a reduced trade deficit) results. c. A stronger exchange rate makes it more difficult for exporters to sell their goods abroad while making imports cheaper, so a trade deficit (or a reduced trade surplus) results. d. A stronger exchange rate makes it more difficult for exporters to sell their goods abroad while making imports cheaper, so a trade surplus (or a reduced trade deficit) results.
Suppose you place $10,000 in a retirement fund that earns a nominal interest rate of 9%. If you expect inflation to be 5% or lower, then you are expecting to earn a real interest rate of at least
a. 1.8%. b. 3%. c. 4%. d. 5%.
If substantial up-front investments in advertising campaigns become essential to a successful market entry, the market is most likely to be:
A. a perfectly competitive market. B. a monopoly. C. a monopolistically competitive market. D. an oligopoly.