Suppose that a worker in Country A can make either 10 iPods or 5 tablets each year. Country A has 100 workers. Suppose a worker in Country B can make either 2 iPods or 10 tablets each year. Country B has 200 workers. Suppose Country B's population of workers increased to 600. Which of the following statements is now true?
A. Country B's production possibilities curve has rotated out for only production of iPods.
B. Country B's production possibilities curve has shifted straight out.
C. Country B's production possibilities curve has shifted straight in.
D. Country B's production possibilities are now more limited because of crowding from having more workers.
B. Country B's production possibilities curve has shifted straight out.
You might also like to view...
According to Simon Kuznet's (1958) research, the pattern of immigration in 1865–1914
(a) showed long swings but not the short-term business cycle fluctuations. (b) showed no long swings in the 1820–1860 period, but did show the business cycle. (c) showed both business cycle patterns and long swing patterns. (d) unlike 1820–1860, showed neither short cycles nor long swings, but was instead a steady surge after the Civil War ended.
For a perfectly competitive firm at its long-run competitive equilibrium point
A) P = AR = MR = LATC = SATC = MC. B) P = AR = MR = LATC > SATC = MC. C) P = AR = MR = MC = LATC = AVC. D) P > MR > AR > MC > LATC > SATC.
What is the usual response of firm to an increase in the price of what they sell?
A. An increase in output B. An increase in hiring factors of production C. An increase in the profit level of the firm D. An increase in employment at the firm E. All of these responses are correct.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.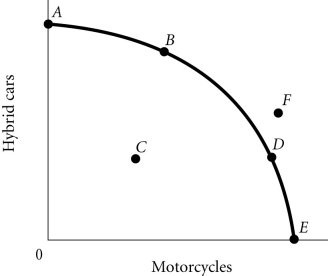 Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, Point F
Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, Point F
A. is efficient and attainable. B. cannot be produced with the current state of technology. C. represents underallocation of resources. D. represents what the people want.