A 6.0-kg object moving 5.0 m/s collides with and sticks to a 2.0-kg object. After the collision the composite object is moving 2.0 m/s in a direction opposite to the initial direction of motion of the 6.0-kg object. Determine the speed of the 2.0-kg object before the collision
a. 15 m/s
b. 7.0 m/s
c. 8.0 m/s
d. 23 m/s
e. 11 m/s
D
You might also like to view...
An incompressible fluid is flowing through a pipe with a constriction. The pipe is on an incline with an angle of 20.0 degrees. The narrow section is 15.0 m from the wide section and the narrow section is lower than the wide section. The velocity of the fluid in the wide section of the pipe is 6.00 m/s and the velocity of the fluid in the narrow section of pipe is 9.00 m/s. The pressure of the fluid in the wide section is 250 kPa. What is the pressure in the narrow section of the pipe? (density of the fluid is 1,000 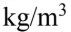
A. 228 kPa B. 203 kPa C. 195 kPa D. 167 kPa E. 145 kPa
A satellite is in a circular orbit 600 km above the Earth's surface. The acceleration of gravity is 8.21 m/s2 at this altitude. The radius of the Earth is 6400 km. Determine the speed of the satellite, and the time to complete one orbit around the Earth.
What will be an ideal response?
A vehicle designed to operate on a drag strip accelerates from zero to 34 m/s while undergoing a straight-line path displacement of 48 m. What is the vehicle's acceleration if its value may be assumed to be constant?
a. 9 m/s2 b. 6.0 m/s2 c. 12 m/s2 d. 18 m/s2 e. 24 m/s2
Monochromatic light shines on a surface with work function 1.80 eV. The maximum energy of the emitted photoelectrons is 0.620 eV. What is the wavelength of the monochromatic light?
A. 200 nm B. 290 nm C. 689 nm D. 602 nm E. 512 nm