Describe the DNA helix structure proposed by Watson and Crick
What is the diameter of the helix and the distance between bases? What types of bonds are involved in stabilizing the DNA backbone, and what types of bonds are found between complementary base pairs? Why would a sequence containing high concentrations of G and C require more energy to break the bonds?
The DNA model contains two DNA polymer strands in a right-handed twist around a common axis. The strands are orientated in an antiparallel direction from 5′ to 3′ and 3′ to 5′. The backbone consists of alternating sugar-phosphate groups stabilized by phosphodiester bonds, and it is located on the outside of the helix. Complementary base pairs are stacked in the center of the helix and are stabilized by hydrogen bonds. There are three hydrogen bonds between G and C, but only two between A and T. Thus, GC-rich regions require higher temperatures to break the bonds. The base pairs, which are perpendicular to the axis, are stacked with 10 base pairs per turn and a helical repeat of 34 The overall diameter of the helix is 10 angstroms.
You might also like to view...
Behavioral responses that animals may or may not use are called facultative
Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
The veins of leaves are used for
a. support. b. identification. c. transport of water and nutrients. d. detachment in the autumn. e. regeneration.
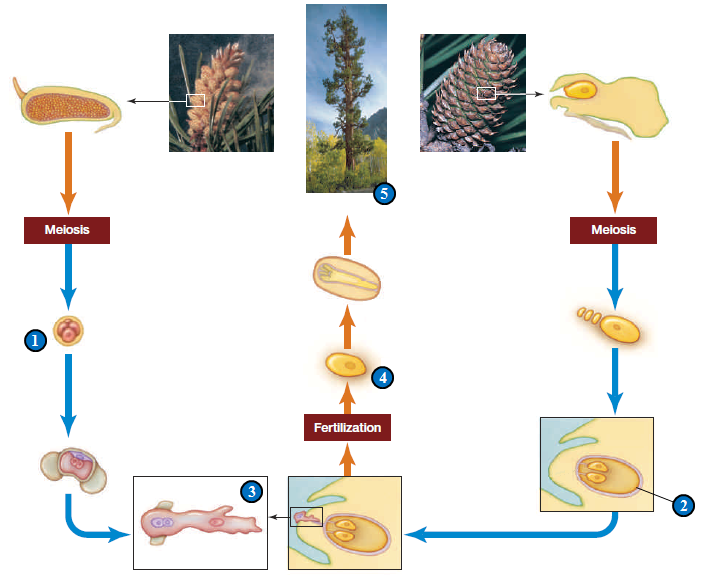
A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 E. 5
Bases have a high ____ concentration
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).