A balance sheet
A) measures flows of income and expenditure over a given period of time.
B) equates flows of revenue with flows of expenditure.
C) measures assets, liabilities, and net worth at a giving instance in time.
D) None of the above are correct.
C
You might also like to view...
Refer to Figure 10.3. An increase in the real interest rate, with no other changes that affect aggregate expenditure, is best represented by ________ in panel (a) and ________ in panel (b)
A) a shift from AE2 to AE3; a shift from IS1 to IS2 B) a shift from AE3 to AE2; a shift from IS2 to IS1 C) a shift from AE2 to AE1; a movement from point B to point A D) a shift from AE3 to AE1; a movement from point C to point A
Constant returns to scale (CRS) implies ________
A) constant returns to labor B) constant returns to capital C) increasing marginal products D) variable total factor productivity E) diminishing marginal products
The Fed buys $1 million in bonds from a bond dealer. The bond dealer's bank experiences
A) an increase in assets of $1 million as its reserves increase and a decrease in liabilities as its transactions deposits fall. B) no change in assets or liabilities. Assets both increased and decreased by the amount of the check. C) a decrease in assets of $1 million as the checking account of the bond dealer increased, and a decrease in liabilities as the bank's deposits with the Fed increased by $1 million. D) an increase in assets of $1 million as its reserves increase and an increase in liabilities of $1 million as the deposits in the bond dealer's transactions account increases by $1 million.
Refer to the diagram in which T is tax revenues and G is government expenditures. All figures are in billions. This diagram portrays the idea of:
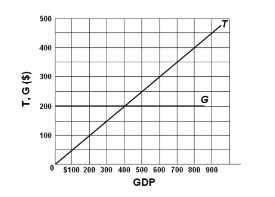
A. progressive taxation.
B. built-in stability.
C. the multiplier.
D. discretionary fiscal policy.