The federal budget is balanced and the economy is on the upward-sloping portion of the Laffer curve. Then, tax rates are cut and government purchases are increased. Is a budget deficit inevitable?
A) No, because a cut in tax rates (on the upward-sloping portion of the Laffer curve) increases tax revenues, and if the increase in tax revenues equals the increase in government purchases there is no deficit.
B) Yes, because a cut in tax rates (on the upward-sloping portion of the Laffer curve) lowers tax revenues.
C) No, because a cut in tax rates (on the upward-sloping portion of the Laffer curve) decreases tax revenues, and if the decrease in tax revenues is less than the increase in government purchases there is no deficit.
D) Yes, because a cut in tax rates (on the upward-sloping portion of the Laffer curve) raises interest rates, and higher interest rates discourage investment spending.
B
You might also like to view...
If a perfectly competitive firm raises the price it charges to consumers, which of the following is the most likely outcome?
A) The firm's total revenue will increase only if the demand for its product is elastic. B) The firm's total revenue will increase only if the demand for its product is inelastic. C) The firm will not sell any output. D) The firm's revenue will not change because some consumers will refuse to pay the higher price.
Forcing a natural monopolist to produce where price, or marginal benefits, equals cost results in an ________ ________ to the monopolist
a. opportunity cost b. economic loss c. economic profit d. normal profit
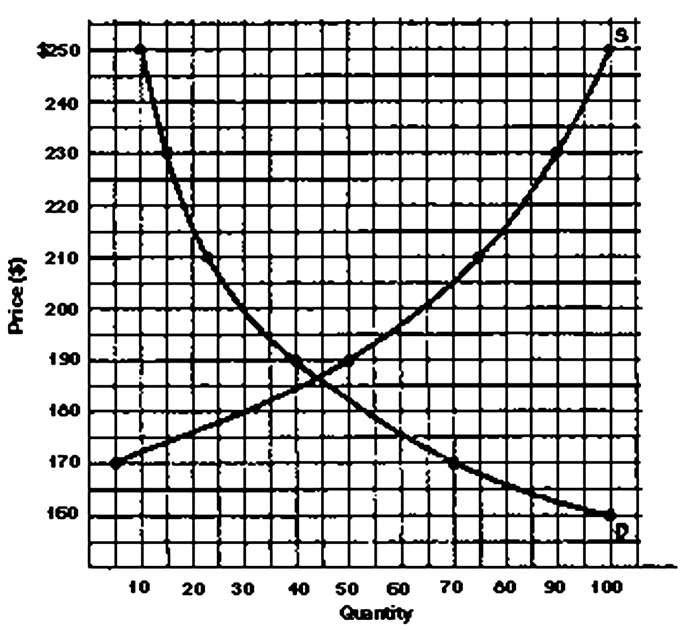
If price were $170, there would be a _____ (shortage or surplus) of _____.
Refer to the table representing Darcy's bank account. Assuming that $1,000 was deposited into her account at the beginning of year 1, and no further deposits or withdrawals were made, the $1,191 value at the end of year 3 represents the:
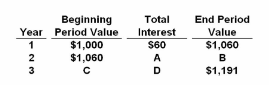
A. discounted value of the $1,000 deposit made at the beginning of year 1.
B. present value of the $1,000 deposit made at the beginning of year 1.
C. future value of the $1,000 deposit made at the beginning of year 1.
D. present value of the interest earned over the three-year period.